- Учителю
- Методическое пособие для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»
Методическое пособие для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»
БЮДЖЕТНОЕ УЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ
ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ ХМАО-ЮГРЫ
НЯГАНСКИЙ ТЕХНОЛОГИЧЕСКИЙ КОЛЛЕДЖ
Методическое пособие
для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»

Авторы:
Саидова И.С. преподаватель английского языка
Бердникова М.Д. преподаватель английского языка
Нягань
2016
Содержание
Аннотация
1.Основная часть……………………………………………………………......4
1.1Краткое содержание пособия………………………………………...…4
1.2 Тема № 1 Computers in our life……………………………….................7
1.3 Тема № 2 Advantages and disadvantages of computers……………..…10
1.4 Тема № 3 What is a computer? ...............................................................12
1.5 Тема № 4 The history and the future of computers……………………..18
1.6 Тема № 5 Computer operations…………………………………….…...20
1.7 Тема № 6 The keyboard………………………………………….……..23
1.8 Тема № 7 Operating systems.The Memory……………………...….......25
1.9 Тема № 8 Commands……………………………………………….…..27
1.10 Тема № 9 The Internet………………………………………………...30
1.11 Тема № 10 Express yourself……………………………………….….34
1.12 Тема № 11 Check your progress……………………………………....34
Заключение
Список использованной литературы
Приложения
Аннотация
Модернизация образования, которая проводится в нашей стране, подразумевает, прежде всего, обновление его содержания. В связи с этим особое внимание уделяется созданию условий для развития творческого личностного потенциала обучающихся и расширению возможностей углубленного образования, в том числе языкового. Такие условия складываются в процессе обучения предмета и овладения знаниями в определенной области на основе взаимосвязанного использования иностранного языка в качестве средства образовательной деятельности.
Методическое пособие предназначено для студентов среднего профессионального образования и обеспечивает содержательную сторону процесса обучения. Учебники английского языка, по которым реализовывается обучение, представляют лексику для профессий технической направленности в целом, специфика для конкретной специальности «Компьютерные сети» отсутствует, что является проблемой для полного и полноценного обучения. Решением этой проблемы мы считаем создание авторского методического пособия, которое восполнит этот образовавшийся пробел. Из вышесказанного следует, что тема разработки актуальна и имеет практическую ценность для всех участников образовательного процесса.
Работа с методическим пособием предполагает всестороннюю активизацию лексико-грамматических конструкций, расширение кругозора обучающихся по своей специальности, обеспечивает личностный рост и мотивирует на дальнейшее изучение профессии, ведь ни для кого не секрет, что компьютер не сказал своего последнего слова.
I. Краткое содержание пособияФормы
контроля
1
Computers in our life.
2
to admire, to call "devil", to deny smth, to work out, to do sums, to write a program, to get some information out from the Internet, to store information, to search for information, to send letters, to chat, to count, to check mistakes, waste of time, to be bad for eyes, like a drug, to use, to keep step with the times, not to be lost in the world of information, to be of great importance, can not tear oneself away from, to be hooked on, to improve, to work on the computer = to operate the computer, to study school subjects on.
Present Indefinite, Present Continuous, to be used for, Word-building
Диалог: Role play between parents and their children.
Монолог: Express your own attitude to computers.
Обсуждение: Many teenagers say "I can't imagine my life without computers"
Do you agree with them? Why?
Чтение текстов «I enjoy computer»,
«The rapid development of Science and Technology ..»
Монолог, диалог, вопросно-ответные упражнения,
грамматический тест, упражнения по тексту.
2
Advantages and disadvantages
1
to safe time, employees,
to lose due (job), to lead (led, led), storage place, to keep data,
to hold an information, to depend on, to enable, to cause problems, eye strain, tool, to serve, to replace.
Present Indefinite, Present Continuous
Монолог: «Advantages and disadvantages of computers» (Express your own attitude).
Чтение текста «Advantages and disadvantages of computers»
Эссе
Монолог, эссе, упражнения по тексту, грамматический тест.
3
What is a computer?
2
electronic machine, form, multimedia, printer, monitor, CD-ROM, modem, processor, instruction, cursor, program, virus, scanner, file, chip, to access, central processing unit (CPU),to crash, database, hardware, process, software, memory, loudspeaker, input, CDH, output, floppy disk, to store information, hard disk, mouse, device, mouse pad, to consist of, keyboard, storage, procedures, copy the text, cut something, open a new document, paste something, print the text, save the document, back up copy, Desktop, My Documents, My Computer, Recycle Bin, Taskbar, Folder, File.
Passive Voice
Аудирование диалога
Монолог: «You are a teacher of Information Technology. Tell your students about the device of computers»
Чтение текстов:
«The term "computer" is used to...» «Computers are electronic machines ...»
Словарный диктант
Обсуждение прослушанного диалога, монолог, лексические и грамматические тесты, упражнения по тексту, словарный диктант.
4
The history and the future of computers
1
device, process, conceived, forerunner, veritable, search engine, Y2K, cheesy
Passive Voice
Монолог: As any human invention, computers have brought about new words - and new problems. Do you agree with this statement?
Обсуждение: Discuss with your classmates the future of computers.
Чтение текста «The history and the future of computers»
Write a time capsule.
Think what will happen to books and computers in 10 years' time.
Монолог, упражнения по тексту, упражнение на закрепление грамматического материала, лексический тест, сообщение.
5
Computer operations
1
arithmetic, procedures, determine,
to benefit from, logical operation,
addition, to embed, subtraction,
flexible, value
Passive Voice, Past Perfect, числитель-ные.
Чтение текста
«Computer operations»
Упражнения: по тексту, грамматические и лексические тесты.
6
The keyboard
1
TAB, BCSP, ENTER, CTRL, SHIFT, HOME, CAPSLOCK, alt="Методическое пособие для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»", PGUP, PGDN, DEL, BREAK, INS, PAUSE, PRTSCP, ESC, NUMLOCK, END
Modal Verbs, the verbs to be and to have.
Лексические и грамматические тесты.
7
Operating systems. The memory.
1
circuit, switch, ON, OFF, binary notation, character, ASCII, bit, byte, KB, MB, GB, RAM.
Comparison of Adjectives
Монолог: Tell your classmates about operating systems and the memory of computers. Why are they used for?
Чтение текста «An operating system tells...»
Лексические и грамматические тесты, монолог, упражнения по тексту.
8
Commands
1
File - New, File - Open, File - Save, File - Save As, File - Page Setup, File - Print, File - Print Preview, File - Properties, File - Exit, Edit - Undo, Edit - Redo, Edit - Cut, Edit - Copy, Edit - Paste, Edit - Delete, Edit - Select All, Edit - Find, Edit - Paste Special, Edit - Replace, Edit - Go To, View - Toolbars, View - Zoom, Insert - File, Insert - Picture, Insert - Object, Format - Font, Format - Paragraph, Format - Style, Tools - Spelling, Tools - Macro, Tools - Customize, Tools - Options, Window - Split
Word-building, Passive Voice, Present, Past, Future Tenses, Imperative sentences.
Перевод слов и предложений, грамматический тест.
9
The Internet
2
WWW - World Wide Web, to retrieve, network, to share, humanities, business transactions, access, to browse, browser, to provide, provider, broadcast live, site, to link, hyperlink, e-mail, to e-mail, to surf the net, search.
Word-building
Аудирование «The History of the Internet»
Обсуждение: What is the Internet? Why do we use it? Is the Internet important in our life? Is it harmful?
Чтение текста «Introduction to the WWW and the Internet».
Чтение инструкции по поиску информации в Интернете
Электронное письмо
Контроль аудирования (тест), диалог, электронное письмо, лексические и грамматические тесты, упражнения по тексту.
10
Express yourself
2
Обсуждение проектов.
11
Check your progress
1
Контроль знаний учащихся
ИТОГО 15
ТЕМА № 1. Computers in our life.
Лексический материал: to admire, to call "devil", to deny smth, to work out,
to do sums, to write a program, to get some information out from the Internet, to store information, to search for information, to send letters, to chat, to count, to check mistakes, waste of time, to be bad for eyes, like a drug, to use, to keep step with the times, not to be lost in the world of information, to be of great importance, can not tear oneself away from, to be hooked on, to improve, to work on the computer = to operate the computer, to study school subjects on.
Грамматический материал: сравнение Present Indefinite и Present Continuous, повторение структуры to be used for, образование новых слов с помощью суффиксов и префиксов (Word-building)
Формы проведения: ознакомление с новой лексикой, активизация употребления новой и ранее изученной лексики по данной теме, ролевая игра, чтение текстов с полным пониманием содержания, их обсуждение, короткие сообщения обучающихся, повторение грамматического материала.
Формы контроля: контроль навыков устной речи (монолог, диалог), контроль понимания содержания текстов (вопросно-ответные упражнения), упражнения на закрепление грамматического материала (тесты).
Занятие №1.
Computers in our life.
Warm up
Hello everybody! Glad to see you. Today we shall begin to study the new course "English and Computer". At our first lesson we shall speak about the role of computers in our life. Computers has become an important part of our life - one can admire it, one can call it "devil", but no one can deny it.
W hat
do you think of computers?
hat
do you think of computers?
Do you play computer games?
Do you study with the help of computer?
Can you write computer programs?
Vocabulary
1) Learn the words
-
to admire - восхищаться
-
to call "devil" - называть «дьяволом»
-
to deny smth - отрицать что-либо
-
to work out - разрабатывать
-
to do sums - решать примеры
-
to write a program - писать программу
-
to get some information out from the Internet - получить информацию из Интернета
-
to store information - хранить информацию
-
to search for information - искать информацию
-
to send letters - посылать письма
-
to chat - болтать
-
to count - считать
-
to check mistakes - проверять ошибки
-
waste of time - пустая трата времени
-
to be bad for eyes - плохо для глаз
-
like a drug - подобно наркотику
2) Fill in the mind map

Grammar
Use Present Indefinite or Present Continuous.
-
It is Monday. I (to help) Helen to choose CD.
-
Carl always (to play) computer games.
-
I still (to look for) some information in the Internet.
-
She often (to use) computer to do her homework.
-
The Internet centre (to open) at nine o'clock.
-
Bill and John (to repair) their printer at the moment.
-
The rate of computer crimes (to increase) quickly.
Role play
Parents often dislike computer games. Have a conversation with a friend: you are the parent, and your friend is a fan of computer games. Use these phrases:
Parent: waste of time/ bad for your eyes/ like a drug/ you can't stop playing it/ boring/ the music is terrible/ you're not doing your homework/ why not to do something else for a change?
Daughter or son: exciting/ educational/ you learn about computers/ your reactions get faster/ important for you/ You want to be a computer programmer/It's OK as you haven't got any homework.
Reading
Read the text and answer the questions:
1. Are the boys computer fans?
2. Where are the boys from?
3. How old are they?
4. What is a PC?
5. What the teenagers think about computers?
6. How do they use them?
I enjoy computer
Patric (Dublin, Ireland):
Don't call it a craze. Ok, computer games are quite new. But now they are with us for ever. Kids are always going to play computer games. I have computer games, a Sega Magadrive. But now I usually play on my Mum's computer. It's a PC - "a personal computer". The games are more complicated and interesting. Look at this one - Helicopter Attack. First you plan your attack. The plan is a very important part of the game. You choose your missiles and lots of other things. You can go over the desert, the forest or the sea. You have radar. And listen to the sound effects - just like a real helicopter!"
Martin (Melbourne, Australia):
I really enjoy writing programs. It sounds difficult. But even an eight-year-old can write a simple program. One of my programs can play chess. It can beat my Mum. She's an excellent chess-player. I sometimes write games. "Scramble" is my latest word game - a bit like a crossword puzzle. You get points for each letter. It's simple - but it works.
Talking
1) Express your own attitude to computers.
2) Give your own definition to the following:
Computer game; Computer program; Craze
Занятие № 2.
Computers in our life.
Warm up
1) In what school subjects can computers be especially important? What for?
2) In what areas of your studies can you easily do without computers?
Vocabulary
1) Learn the words
-
to use - использовать, применять
-
to keep step with the times - жить в ногу со временем
-
not to be lost in the world of information - не потеряться в мире информации
-
to be of great importance - иметь важное значение
-
can not tear oneself away from … - не могут оторваться от …
-
to be hooked on … - не представлять себе жизнь без …
-
to improve - улучшить
-
to work on the computer = to operate the computer - работать на компьютере
-
to study school subjects on … - изучать школьные предметы по …
Reading
Read the text and answer the questions.
-
Where have computers been used in recent years?
-
Why are they of great importance at the present time?
-
Where do people use computers?
-
Why are children especially hooked on them?
-
Do you like to operate the computer?
The rapid development of Science and Technology has changed the world. In recent years computers have been used in all fields of human activities: business, industry, education, culture, health care service, economics, politics, mass media, arts, in everyday life of different people. At the present time people have to keep step with the times and not to be lost in the world of information. So computers are becoming of great importance for most adults and youth.
Nowadays more and more people use computers at work and home. They can not tear themselves away from their computers. Especially children and teenagers are hooked on them. They like to play computer games and spend hours with educational programs. More and more kids can improve their reading, writing and arithmetic when they operate the computer. Many students study school subjects on it. They say computers make leaning fun!
Grammar
1) Translate the words. Pay attention to the suffices and prefixes.
1. develop developing development developed
2. provide providing provision provided
3. defend defense defensive defended
4. depend dependent dependence depended
5. possible possibly possibility impossible
6. destroy destructive destruction destroyed
7. act actual action acted
8. produce product productive production
2) Complete the table
Talking
Many teenagers say "I can't imagine my life without computers"
Do you agree with them? Why?
ТЕМА № 2. Advantages and disadvantages of computers.
Лексический материал: to safe time, employees, to lose due (job), to lead (led, led), storage place, to keep data, to hold an information, to depend on, to enable, to cause problems, eye strain,, tool, to serve, to replace.
Грамматический материал: повторение грамматического материала Present Indefinite и Present Continuous
Формы проведения: Введение и закрепление новой лексики, чтение текста с пониманием основного и общего содержания, его обсуждение, повторение грамматического материала, краткие сообщения обучающихся, повторение устойчивых выражений, написание эссе.
Формы контроля: контроль навыков устной (монолог) и письменной (эссе) речи, контроль понимания содержания текста (упражнения по тексту), упражнения на закрепление грамматического материала (тест).
Warm up
1) What are computers used for?
2) What is the role of computers in our life"
Grammar
Underline the correct tense.
-
More and more people buy/are buying their own computers these days.
-
Sheila works/is working as a web designer for the local companies.
-
Computer holds/is holding a five-day seminar on computers for all its employees.
-
Lauren doesn't leave/isn't leaving her house before 9 o'clock in the morning.
-
No wonder the phone bills are so high! You always talk/are always talking on the phone!
-
I don't teach/am not teaching in the evenings at present.
-
Do amphibians live/Are amphibians living both on land and in water?
-
I never go/am never going to that Internet cafe again! The speed of connection was horrible!
-
They prefer/are preferring to go to the Internet centre in the morning when it is less crowded.
-
Chris and Helen are having/have a garden party on Sunday afternoon.
Vocabulary
-
to save time - экономить время
-
employees - служащие
-
to lose due (job) - терять должность (работу)
-
to lead (led, led) - вести
-
storage place - место хранения
-
to keep data - хранить данные
-
to hold an information - содержать информацию
-
to depend on - зависеть
-
to enable - позволять
-
to cause problems - причинять проблемы
-
eye strain - напряжение глаз
-
tool - инструмент
-
to serve - служить
-
to replace - заменять
Reading
Two "for and against" argumentative essays were mixed by a typist. Divide this text in two parts, one is "for", another is "against":
Advantages and disadvantages of computers.
One of the main advantages is the time that can be saved by using a computer. This especially beneficial in the workplace where employees can do their work far faster than they could in the past. Many jobs have been lost due to the fact that computers can do a lot of tasks more efficiently than humans. This has led to high unemployment in many countries.
Computers can save a lot of storage space. Storing information on computer disks is one of the most efficient ways of keeping data. One computer disk can hold the same amount of information as several books.
Stored information can be found at the touch of a button, whereas searching for it manually takes much longer. We have become too dependent on computers. The time saved by using PC for repetitive tasks enables us to use our own time more creatively and productively.
Computers can actually cause health problems. Endless hours in front of a screen can cause eye strain and headaches. Our everyday lies are made easier - from going to the bank to doing the shopping.
Computers are a useful tool. They have changed our lives for the better and we should make them work to our advantage. It must be remembered that they are to serve us - not to replace us.
Talking
Topic: Advantages and disadvantages of computers. (Express your own attitude).
Writing
1) Write down the expressions "for and against computers" in two columns.
2) Some people consider that computers should be used more and more extensively. Some people think that computers are harmful and should not be used so much. Write an essay on the topic using following expressions.
I'd like to tell…
It is devoted to the problem of….
In the first place…
In addition to this…
However…
What is more…
To sum up…
Furthermore…
Therefore…
Nevertheless…
All in all…
ТЕМА № 3. What is a computer?
Лексический материал: electronic machine, form, multimedia, printer, monitor, CD-ROM, modem, processor, instruction, cursor, program, virus, scanner, file, chip, to access, central processing unit (CPU), to crash, database, hardware, process, software, memory, loudspeaker, input, CDH, output, floppy disk, to store information, hard disk, mouse, device, mouse pad, to consist of, keyboard, storage, to accept, to refine, procedures, copy the text, cut something, open a new document, paste something, print the text, save the document, back up copy, Desktop, My Documents, My Computer, Recycle Bin, Taskbar, Folder, File.
Грамматический материал: употребление и образование Present Passive Voice.
Формы проведения: ознакомление с новой лексикой в том числе со специальными терминами, перевод интернациональной лексики, активизация употребления новой лексики с помощью различных упражнений, чтение текстов с извлечением полной информации, их обсуждение, аудирование диалога, повторение грамматического материала, краткие сообщения обучающихся, словарный диктант
Формы контроля: контроль навыков аудирования (обсуждение диалога), устной речи (монолог), упражнения на закрепление лексического и грамматического материала (тесты), контроль понимания содержания текстов (упражнения по тексту), словарный диктант.
Оборудование: компьютер
Занятие №1.
What is a computer?
Vocabulary
1) Read the words and translate them.
electronic machine, form, multimedia, printer, monitor, CD-ROM, modem, processor, instruction, cursor, program, virus, scanner, file, chip.
2) Learn the new words.
to access -выборка , доступ, обращение
central processing unit (CPU) - центральное процессор. устройство
to crash - ломаться
data(base) - данные, информация
hardware - аппаратное обеспечение
process - процесс, прием, режим,
software - программное обеспечение
convert- обрабатывать
memory - память
loudspeaker - звуковые колонки
input - ввод, входное устройство
CDH - диск
output - вывод, выводное устройство
floppy disk - дискетка
to store information - хранить информацию
hard disk - жесткий диск
mouse - мышь
device - устройство
mouse pad - коврик для мышки
to consist of - состоять из
keyboard - клавиатура
procedures - процедуры (действия)
to accept - принимать
to refine - очищать
storage - хранение, запоминающее устройство
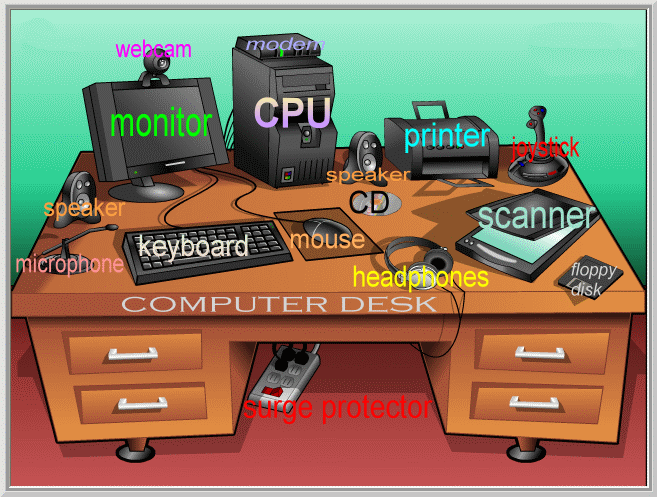
3) Recall the names of the objects in the picture.
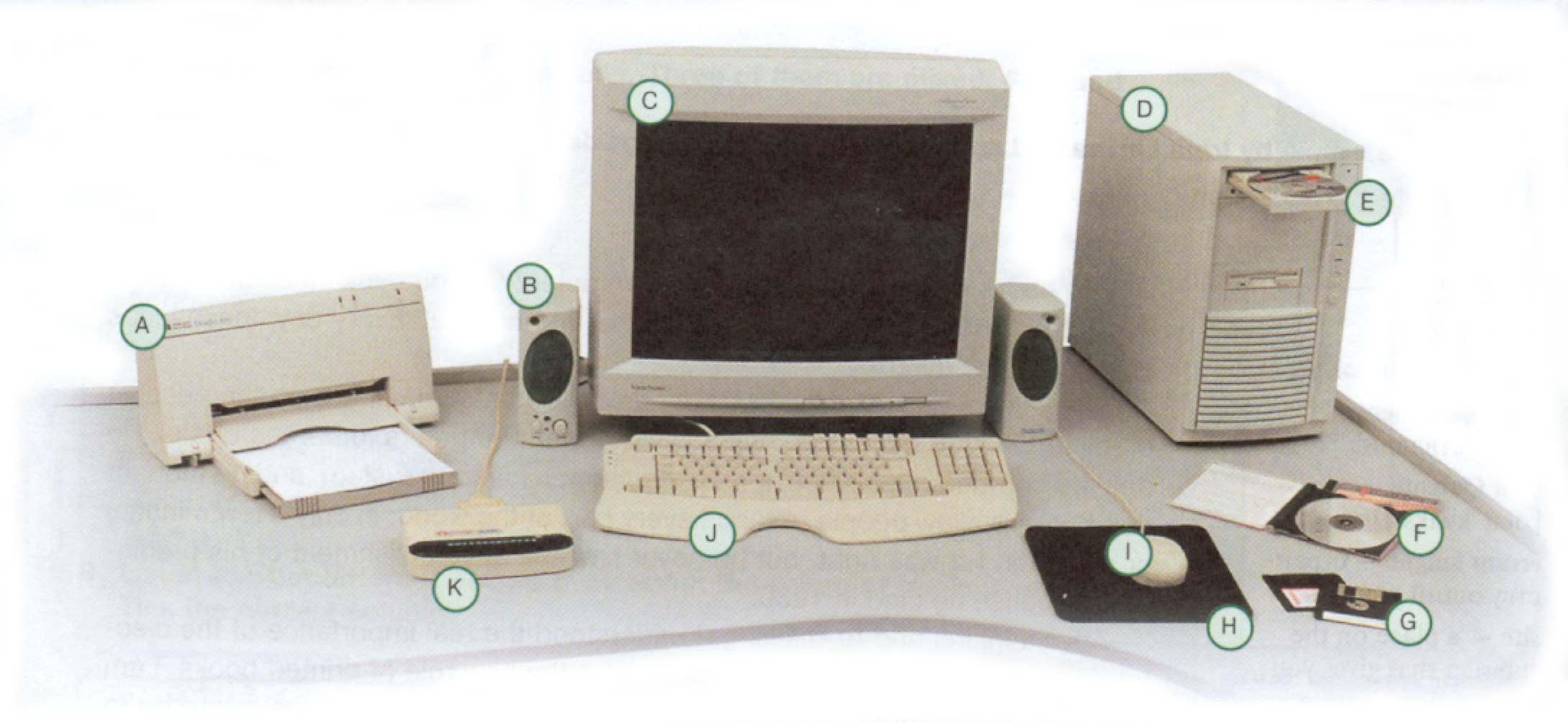

4) Look at the words and say what is software and what is hardware.
program mouse pad instruction symbol results on the monitor
mouse printer information cursor scanner
CPU modem keyboard memory process data
5) Find the synonyms.
1. product a. screen
2. monitor b. electronic machine
3. data c. information
4. computer d. result
5. memory e. storage
Reading
1) Read the text.
The term "computer" is used to describe a device for processing information at high speed by electronic means. Computer has no intelligence by itself and is referred to as hardware. A computer system is a combination of five elements:
-
Hardware
-
Software
-
People
-
Procedures
-
Data /Information
Software is the term used to describe the instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task. Without software instructions, the hardware doesn't know what to do. People, however, are the most important component of the computer system: they create the computer software instructions and respond to the procedures that those instructions present.
The basic job of the computer is the processing of information. Computers accept information in the form of instructions called programs and symbols called data to perform mathematical and logical operations and then give the results (information). The data is raw material while information is organized, processed, refined and useful for decision making. A computer is used to convert data into information. A computer is also used to store information in the digital form.
2) Answer the questions.
1. What does the term "computer" describe?
2. Is computer intelligent?
3. What elements does the computer consist of?
4. What is hardware?
5. What is software? What is the difference between hardware and software?
6. Why people are the most important component of the computer system?
7. How does a computer convert data into information?
3) Complete the sentences.
1. The basic job of the computer is the ...
2. Information in the form of instruction is called a ...
3. ... is the term used to describe the instructions that tell the hardware how to perform a task.
4. A computer is used to convert data into ...
5. A computer is used to ... in the digital form.
4) Read and say if the sentences are true or false.
1. A computer is made of electronic components so it is referred to as an electronic device.
-
A computer has no intelligence until software is loaded.
-
There are four elements of a computer system.
-
Without software instructions, the hardware doesn't know what to do.
-
Software is the most important component because it is made by people.
5) Describe computer devices.
Grammar
Paraphrase the following sentences. Use the Passive Voice.
-
We use computers to teach courses such as language learning, programming, mathematics.
-
The directory on each disk keeps the names of our files.
-
We can give a unique name for each file.
-
We store each filename in a directory.
-
People pay for their E-mail service.
-
Computers accept information in the form of instructions.
Talking
You are a teacher of Information Technology. Tell your students about the device of computers.
Занятие № 2.
What is a computer?
Listening
1) Listen to the dialogue. Answer the question: ''What problem with the computer did Helen have? (Приложение 1)
Some useful expressions: to be computer-literate-уметь работать на компьютере; to lose one's work-потерять результаты своей работы; back up copy-запасная копия; old-fashioned-старомодный, устарелый; user-friendly-удобный для пользователя.
2) Now think a little over and say, what could Helen do with a text in her computer?
Vocabulary
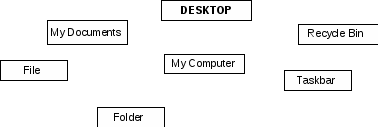
1) Let's switch on our computers. Can you see the Desktop? What is located on the Desktop?
-
Desktop - рабочий стол
-
My Documents - Мои документы
-
My Computer - Мой компьютер
-
Recycle Bin - корзина
-
Taskbar - панель задач
-
Folder - папка
-
File - файл, документ
2) Match a word from box A with a word from box B to form eight words or expressions connected with computer.B: speaker pad - ROM base ware disk board put
3) Match the definition with the correct spelling word.
1. The combination of sound, graphics and video to present
information on a computer
2. System of storing information in a computer on magnetic tape, etc.; storage
3. A computer program that is designed to replicate itself by copying itself into the other programs stored in a computer (often with a negative effect).
4. A large amount of information stored in computer system
5. Information or instructions put into a computer
6. Information put out by or delivered by a computer
7. Programs that run a computer
8. An input device that is moved around the desk top to control the position of the cursor on the display screen.
9. An electronic machine that can store, recall, or process information
10. The computer's machinery - the parts you can see and touch, like the monitor and all the electronic devices and circuits inside it.
11. A small removable magnetic disc which is used to store data
a. computer
b. hardware
c. mouse
d. memory
e. database
f. floppy disk
g. input
h. virus
i. multimedia
j. software
k. output
Reading
1) Read the text.
2) Name three basic steps which are involved in the process.
3 )
Name three main sections of the computer. What are their functions?
)
Name three main sections of the computer. What are their functions?
Computers are electronic machines which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the processing as information.
Three basic steps are involved in the process: First, data is fed into the computer's memory. Then, when the program is run, the computer performs a set of instructions and processes the data. Finally, we can see the results (the output) on the screen or in printed form.
A standard computer system consists of three main sections: the Central Processing Unit, the main memory and the peripherals.
Central Processing Unit is the "brain" of the computer. Its function is to execute program instructions and coordinate the activities of all the other units. The main memory holds the instructions and data which are processed by the CPU. The peripherals are the physical units attached to the computer. They are input devices (mouse, keyboard), output devices (monitor, printer), storage devices (floppy or hard discs).
Storage devices provide a permanent storage of both data and programs. Disk drives are used to handle one or more floppy disks. Input devices enable data to go into the computer's memory. The most common input devices are the mouse and the keyboard. Output devices enable us to extract the finished product from the system. For example, the computer shows the output on the monitor or prints the results onto paper by means of a printer.
On the rear panel of the computer there are several ports into which we can plug a wide range of peripherals - modems, fax machines, optical drives and scanners.
These are the main physical unites of a computer system, generally known as the configuration.
In pairs, choose one of these input devices and describe its functions and features. Try to guess which device your partner is describing.
ТЕМА № 4. The history and the future of computers
Лексический материал: device, process, conceived, forerunner, veritable, search engine, Y2K, cheesy.
Грамматический материал: употребление и образование Passive Voice.
Формы проведения: ознакомление с новой лексикой, активизация употребления новой и ранее изученной лексики по данной теме, чтение текста с извлечением необходимой информации, его обсуждение, короткие сообщения обучающихся, повторение грамматического материала, написание сообщения.
Формы контроля: контроль навыков устной речи (монолог), контроль понимания содержания текста (вопросно-ответные упражнения, множественный выбор, правильно-неправильно), упражнения на закрепление грамматического материала (тесты), контроль письменной речи (сообщение).
Warm up
What do you know about computers? In pairs or groups, answer the following questions.
-
When was the first computer invented?
-
In which country did it first appear?
-
What are its main functions today?
-
How is it used at school?
-
What do you know about Y2K?
-
What's a bug? How many meanings of this word do you know?
After you have tried to answer these questions, check the answers with your teacher.
Vocabulary.
Today's article has some new words. Match the words with the most suitable meanings.
Reading.
1) You are going to read an article about computers. Read the article quickly to see which topics are discussed.
-
The invention of a computer.
-
The Internet and its modern usage.
-
Personal Computers.
-
Banking.
2) What other topics are discussed in the article?
T he
history and the future of computers
he
history and the future of computers
Computer information have been a part of everyday life for more than a generation. It is believed that the principles behind the modern computer were first conceived by Charles Babbage (1792-1871), a British mathematician and inventor. Babbage tried to build a machine which could store information and produce more accurate mathematical calculations and tables. He could not finish it for lack of the appropriate materials, but his attempt was a real forerunner of the twentieth century invention.
T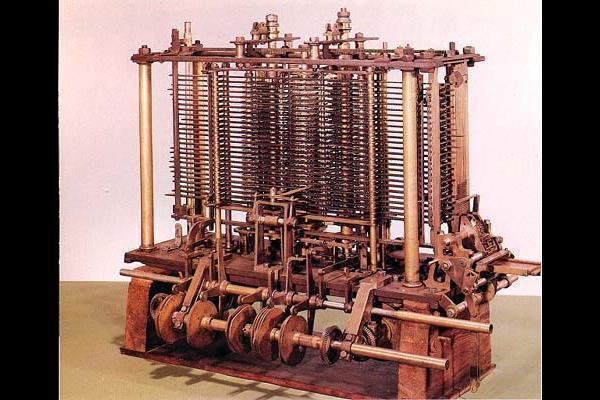 he
first practical machines were built in Great Britain and the USA
during World War II. In the next twenty years, with the invention
of the transistor, a veritable revolution in the computer science
had occurred. Since the 1970's, with the invention of silicon
chips, computers have become a part of, and even a way of life for
many people.
he
first practical machines were built in Great Britain and the USA
during World War II. In the next twenty years, with the invention
of the transistor, a veritable revolution in the computer science
had occurred. Since the 1970's, with the invention of silicon
chips, computers have become a part of, and even a way of life for
many people.
In 1969, the first connection between two computers was established in the USA. That year is considered to be the birth year of the Internet and the World Wide Web (WWW). By the year 2000, the whole world has become one large network. As some people joke, nobody understands what the Internet is, yet everybody uses it. However, 91% of the Internet users live in a few developed countries, whereas in some developing countries, only 1% of the population has Web access.
As any human invention, computers have brought about new words - and new problems. To use the computer and the Internet today, one must understand not only which buttons to press when. There are lots of terms which a layman should master. Press enter, search engine, virus, bug are only a few examples.
The very end of the twentieth century is marked by Y2K, a mysterious virus which nobody has witnessed, but which lots of people are apprehensive about. By the way, this abbreviation is well known in the USA and some other countries, but in the UK, they call it Virus 2000.
Another phenomenon is spam, machine-generated junk mail, which includes chain letters, advertisements, cheesy magazine pictures etc. Imagine your mail box being suddenly stuffed with more than 5,000 letters a day!
Before the advent of computers, banks were afraid of robbers. Today, hackers may be a much greater menace. With a flick of a finger, a few typed digits, any bank may lose millions. Yet, in spite of all the hazards, mankind uses the computer everyday, and will continue doing so for some time to come.
Article Nina M. Koptyug, 1999
3) Read the article carefully.
4) True, False, Not Mentioned?
Read the following statements and write T if the statement is true
according to the article, F if the statement is false, and NM if
the article does not give that information.
-
Computers were first invented in 1990.
-
They were invented in Britain.
-
Computers are used in mathematics only.
-
All the countries are now connected to the Internet.
-
Any user must know some terms.
-
There is a world computer program for dealing with Y2K.
Grammar
Find all the sentences in the text where the Passive Voice is used.
Change them into Active.
Talking
1) As any human invention, computers have brought about new words - and new problems. Do you agree with this statement?
2) Discuss with your classmates the future of computers.
Writing
You are going to write a time capsule.
-
Think what will happen to books and computers in 10 years' time.
-
Write a paragraph on a piece of paper and keep it in a safe place.
-
Read it in 10 years to see if you were right.
ТЕМА № 5. Computer operations
Лексический материал: arithmetic, procedures, determine, to benefit from, logical operation, addition, to embed, subtraction, flexible, value.
Грамматический материал: совершенствование навыков употребления Passive Voice, повторение Past Perfect, образование и употребление числительных.
Формы проведения: введение и закрепление новой лексики, чтение технического текста с извлечением необходимой информации, обсуждение текста, выполнение грамматических упражнений.
Формы контроля: контроль понимания текста с помощью различных упражнений: ответить на вопросы, «правильно-неправильно», закончить предложения; упражнения на закрепление грамматического материала (тесты).
Computer Operations
Warm up
1) What can we do with a text in computer?
2) What is a computer?
Vocabulary
Choose the right variant
-
Computers can help to ______ mathematical operations and solve different problems.
a. feed b. accept c. perform d. store
-
Electronic machines _______ information on disks in files.
a. involve b. store c. execute d. process
-
Laser printers produce ________ at great speed.
a. configuration b. output c. memory d. data
-
Software is ______ in the form of data and programs.
a. memory b. unit c. information d. floppy disk
-
Peripherals consist of _______ and input/ output devices.
a. software b. data c. storage devices d. certain form
Reading
1) Read the text and try to translate the following words.
arithmetic procedures
determine
to benefit from
logical operation
addition
to embed
subtraction
flexible
value
Computer Operations
Much of the processing computers can be divided into two general types of operation. Arithmetic procedures. Early computers performed mostly arithmetic operations, which gave the false impression that only engineers and scientists could benefit from computers .Of equal importance is the computer operations are computations with numbers such as addition, subtraction, and other mathematical ability to compare two values to determine if one is larger than, smaller than, or equal to the other. This is called a logical operation .The comparison may take place between numbers, letters, sounds, or even drawings The processing of the computer is based on the computer's ability to perform logical and arithmetical operations.
Instructions must be given to the computer to tell it how to process the data it receives and the format needed for output and storage. The ability to follow the program sets computers apart from most tools.
However, new tools ranging from typewriters to microwave ovens have embedded computers, or build-in computers .An embedded computer can accept data to use several options in its program, but the program itself cannot be changed. This makes these devices flexible and convenient but not the embedded computers itself.
2) Answer the questions for general understanding:
-
In what two major parts could be computer operations divided?
-
What are arithmetic operations and what are logical operations?
-
What are embedded computers?
-
What modern devices have embedded?
-
What makes computer so different from other tools?
3) Which sentences are true and which are false?
-
Arithmetic operations are operations with numbers-subtraction and division.
-
Early computers gave false impression about their capabilities.
-
Logical operations are computer's ability to compare two values.
-
The major difference between the computer and tools lies in the flexibility of the program.
-
Microwave oven's program is flexible and could be changed because of the embedded computer.
4) Complete the following sentences. Work individually, consult the text.
-
The computers ability to compare two values to determine if one is larger than, smaller than or equal to the other is called…. .
-
New tools ranging from typewriters to microwave ovens have embedded computers or……….computers.
-
……….are computations with numbers such as addition, subtraction and other mathematical procedures.
Grammar
1) Find the sentences in the text where Passive Voice is used.
2) Arithmetic operation deals with numbers. Translate the sentences from Russian into English. Read the numerals correctly.
-
There are two formats for floppy disks 5.25' and 3.5'.('-inch-дюйм)
-
3.5' disks are formatted 1.4 MB are widely used.
-
The major chip is known as the 8255.
3) Using the words from the right, answer the Past Perfect questions:
Complete the sentence:
Up to the time the first digital computer was completed in 1944:
2. How had letters been written?
3. How had companies stored information?
4. How had information been exchanged?
5. How had office clerks processed information?
6. What hadn't people had big problems with?
7. What had industrial productions required?
8. What had only a few people considered possible?
9. Who hadn't had the possibility to correct texts immediately?
10. What had blue collar workers needed?
a. secretaries
b. data protection
c. by mail or phone
d. fingers or mechanical devices
e. the development of "intelligent" machines
f. on mechanical typewriters
g. some computer knowledge
h. far more labour
i. quite slowly
j. on large quantities of paper
ТЕМА № 6. The keyboard
Лексический материал: TAB, BCSP, ENTER, CTRL, SHIFT, HOME, CAPSLOCK, alt="Методическое пособие для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»", PGUP, PGDN, DEL, BREAK, INS, PAUSE, PRTSCP, ESC, NUMLOCK, END.
Грамматический материал: употребление модальных глаголов, функции глаголов to be и to have.
Формы проведения: ознакомление с новой лексикой в том числе со специальными терминами, активизация употребления новой лексики, выполнение грамматических упражнений, практическая работа: набор текстов на английском языке
Формы контроля: упражнения на закрепление лексического и грамматического материала (тесты).
The Keyboard.
Vocabulary
BCSP = BACK SPACE (место сзади) - стирание символа, находящегося слева от курсора.
BREAK (ломать, прерывать) - эта клавиша позволяет прервать работу программы.
CAPS LOCK = CAPITAL (прописная буква) LOCK - режим печати заглавных букв на дискете.
DEL = DELETE (стирать) - применяется, чтобы стереть символ, на который указывает курсор.
ENTER (входить) - нажимается для ввода в компьютер строки или команды.
ESC = ESCAPE (убегать) - используется для того, чтобы выйти из текущего режима работы.
HOME (домой) - клавиша позволяет вернуть курсор в начало строки.
INS = INSERT (вставлять) - включение и выключение режима вставки на экране дисплея.
NUM LOCK = NUMBER (число) LOCK - клавиша фиксации цифр.
PGDN = PAGE DOWN (страница ниже) - «прокрутка» изображаемого текста на один «экран» вниз.
PGUP = PAGE UP (страница выше) - «прокрутка» изображаемого текста на один «экран» вверх.
SHIFT (сдвигать) - дает возможность «сдвинуть» клавиатуру на верхний регистр для печати отдельных заглавных букв и символов на дисплее.
END (конец, окончание) - используется для перевода курсора в конец строки
TAB = TABULATION (табулирование, составление таблиц) - используется для перевода курсора на определенное количество позиций.
PAUSE - пауза.
alt="Методическое пособие для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»" = alt="Методическое пособие для специальности 09.02.02 «Компьютерные сети»"ERNATIVE - альтернатива.
CTRL - изменение значения последующих клавиш.
PRT SC = PRINT SCREEN - печатает на принтере изображение с экрана дисплея.
1) Match the words from two columns with their definition.
BKSP
CAPS LOCK
PG UP
PRT SC
NUM LOCK
PG DN
1. page down
2. number lock
3. print screen
4. page up
5. capitals lock
6. back space
а. фиксация цифр и перевод малой клавиатуры в режим управления экраном;
b. фиксация режима печати заглавных букв;
c. «прокрутка» текста на экран вверх;
d. «прокрутка» текста на экран вниз;
e. стирание символа, находящегося слева от курсора;
f. печать на принтере образа экрана дисплея.
2) Find the right translation.
1. вводить
2. сдвиг
3. домой
4. ломать, обрывать
5. конец, окончание
escape, insert, enter, end;
home, break, shift, end;
shift, pause, break, home;
escape, break, shift, home
enter, escape, insert, end
3) Match the word with the definition.
DEL a. прерывание работы программы;
b. стирание символа слева от курсора;
c. стирание символа, на который указывает курсор.
INS а. выход из текущего режима работы программы;
b. возврат курсора в начало строки;
c. включение режима вставки символов на экран дисплея.
TAB а. перевод курсора в начало строки;
b. перевод курсора на определенное количество позиций;
c. перевод курсора в конец строки
SHIFT а. фиксация режима печати заглавных букв;
b. сдвиг клавиатуры на верхний регистр для печати отдельных
заглавных букв и символов на дисплее;
c. перевод курсора на определенное количество позиций.
THE KEYBOARD: Label the picture of a standard keyboard with the groups of keys (1-5).
-
Cursor control keysinclude arrow keys that move the insertion point up, down, right and left, and keys such as End, Home, Page Upand Page Down,which are used in word processing to move around a long document.
-
Alphanumeric keysrepresent letters and numbers, as arranged on a typewriter.
-
Function keysappear at the top of the keyboard and can be programmed to do special tasks.
-
Dedicated keysare used to issue commands or to produce alternative characters, e.g. the Ctrl key or the Altkey.
-
A numeric keypadappears to the right of the main keyboard. The Num Lockkey is used to switch from numbers to editing keys.
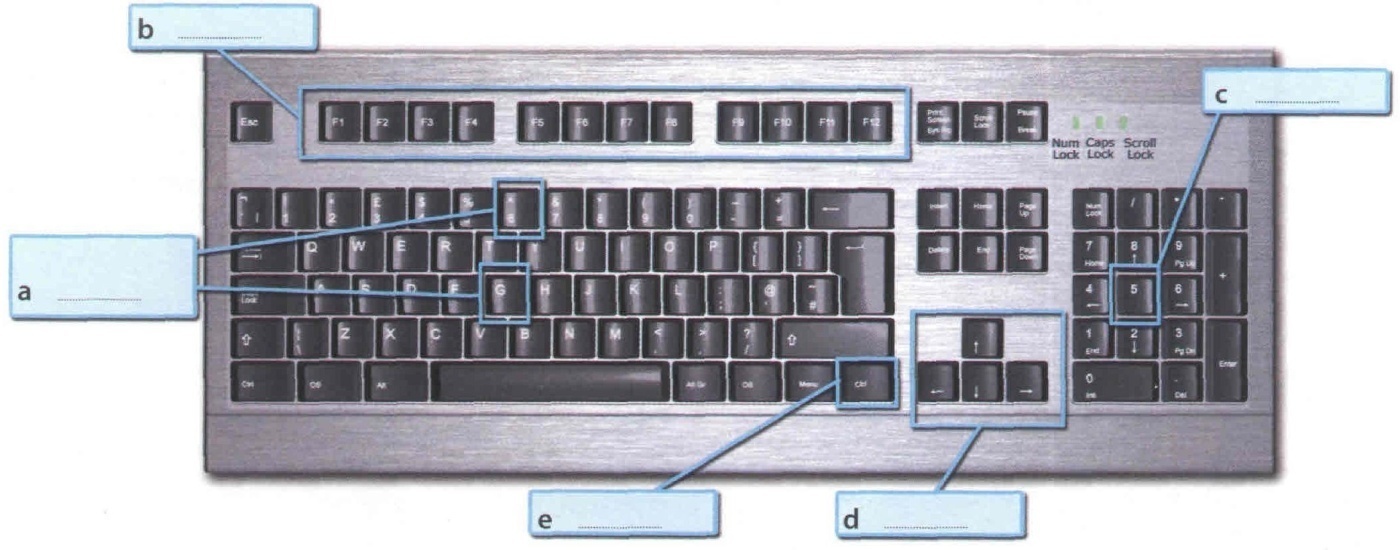
Match the descriptions (1-8) with the names of the keys (a-h).Then find them on the keyboard.A long key at the bottom of the keyboard. Each time it is pressed, it produces a blank space.
It moves the cursor to the beginning of a new line. It is also used to confirm commands.
It works in combination with other keys. For example, you press this key and C to copy the selected text.
It removes the character to the left of the cursor or any selected text.
It produces UPPER CASE characters.
It produces UPPER CASE letters, but it does not affect numbers and symbols.
It moves the cursor horizontally to the right for a fixed number of spaces (in tabulations and data fields).
They are used to move the cursor, as an alternative to the mouse.
a arrrow keys
b return/enter
c Caps Lock
d shift
e tab
f space bar
g backspace
h Ctrl
Grammar
1) Match modal verbs. Translate the sentences.
-
People should help each other.
-
Everybody ought to know safety rules.
-
Any student must know the difference between the digital and analog computer
-
The program has failed. You'll have to change the program.
-
Any firm can benefit from computerization.
-
Any firm can buy computers.
-
Under these conditions you will not be able to control windows and will have to reboot the system.
-
They may take any manual.
-
You may not mix symbols.
-
This computing system must be very effective.
-
A computing system may save time and money.
-
Can a key-name consist of any combination of letters and digits?
2) Translate the sentences. Pay attention to the verbs to be and to have.
-
The new PC is in the next room.
-
This computer is now operating in the net.
-
This problem was solved by the PC.
-
We were to receive the programs yesterday.
-
The Internet has many service programs.
-
The new PC has just been installed in our lab.
-
We have to repeat this experiment.
ТЕМА № 7. Operating systems. The Memory
Лексический материал: circuit, switch, ON, OFF, binary notation, character, ASCII, bit, byte, KB, MB, GB, RAM.
Грамматический материал: повторение Comparison of Adjectives
Формы проведения: введение и закрепление новой лексики, чтение текста с пониманием основного и общего содержания, его обсуждение, краткие высказывания обучающихся по данной теме, повторение грамматического материала.
Формы контроля: упражнения на закрепление лексического и грамматического материала (тесты), контроль навыков устной речи (монолог), контроль понимания текста с помощью различных упражнений.
Operating systems. The Memory
Grammar
Choose the right variant.
1. Both these computers are cheap, but which is ____ ? This one is.
a) more cheap b) much cheap
c) the cheapest d) much more cheaper
2. Which is _______ computer in the shop? This one is.
a) expensive b) expensiver
c) the expensivest d) the most expensive
3. It's ______ processor I've ever seen.
a) fast b) faster
c) the fastest d) more faster
4. John worked _____ than me.
a) harder b) more harder
c) the hardest d) hard
5. Don't buy this modem. It's ______ .
a) much more expensive b) expensiver
c) much more expensiver d) the expensivest
Vocabulary
1) Read the international words.
signal, to group, code, standard, to combine, symbol.
2) Learn the words
circuit - схема
switch - переключатель
ON - включено
OFF - выключено
binary notation - двоичное представление
character - знак, символ, буква
ASCII - Американский стандартный код для обмена информацией
DOS - дисковая операционная система
Reading
1) Read the text and answer the questions.
-
What is an operating system?
-
What operating systems do you know?
-
What is a bit? What is it used for?
-
What is a program?
-
What units are used to describe the RAM memory?
An operating system tells the computer how to understand what jobs it has to do, how to do these jobs, and how to tell people the results. It tells the electronics inside the computer, or "hardware", how to work to get the results it needs. This lets most computers have the same operating system, or list of orders to tell it how to talk to the user, while each computer can have its own computer programs or list of jobs to do what its user needs. Having different programs and operating systems makes it easy to learn how to use computers for new things. When a user needs to use a computer for something different, the user can learn how to use a new program. DOS is the most commonly used PC operating system. Windows NT (new technology) is an operating system developed by Microsoft. Windows 2003, 2007 are the most popular operating systems.
Information is processed and stored in computers as electrical signals. A computer contains thousands of electronic circuit connected by switches that can only be one of two possible states: ON or OFF. To represent these two conditions we use binary notation in which 1 means ON and 0 means OFF. This is the only way a computer can "understand" anything. Each 1 or 0 is called a bit.
1s and 0s represent characters (letters, numbers and symbols). Eight bits together are called a byte. Computers can use many bits together to represent instructions and the data that these instructions use. A list of these instructions is called a program and stored on the computer's hard disk.
The computers use a standard system. This is ASCII (pronounced "ask-key"). There are 256 different ways of combining 0 and 1 bits in a byte. So they can give us 256 different signals.
We also use units such as kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes. One kilobyte (KB) is 1,024 bytes. One megabyte (MB) is 1,024 kilobytes, and one gigabyte (GB) is 1,024 MB. We use these units (KB, MB, GB) to describe the RAM (random access memory - память с произвольным доступом) memory. Computers use memory called "RAM" as a space to carry out the instructions and store data while it is doing these instructions.
When the computer wants to store the results of the instructions for later, it uses the hard disk. Computers store data and the instructions telling them what to do with the data as numbers, because computers can do things with numbers very quickly.
2) Find nouns from the text to the following adjectives.
different
binary
the only
standard
electrical
electronic
possible
3) Translate the following words.
RAM, ON, OFF, KB, MB, GB, DOS, PC, NT
4) Find the main sentences in the text.
Talking
Tell your classmates about operating systems and the memory of computers. Why are they used for?
ТЕМА № 8. Commands
Лексический материал: File - New, File - Open, File - Save, File - Save As, File - Page Setup, File - Print, File - Print Preview, File - Properties, File - Exit, Edit - Undo, Edit - Redo, Edit - Cut, Edit - Copy, Edit - Paste, Edit - Delete, Edit - Select All, Edit - Find, Edit - Paste Special, Edit - Replace, Edit - Go To, View - Toolbars, View - Zoom, Insert - File, Insert - Picture, Insert - Object, Format - Font, Format - Paragraph, Format - Style, Tools - Spelling, Tools - Macro, Tools - Customize, Tools - Options, Window - Split
Грамматический материал: образование слов с помощью префиксов re, un и суффиксов or, er, -tion (Word-building), употребление Passive Voice, Present, Past, Future Tenses, структура повелительных предложений.
Формы проведения: ознакомление с новой лексикой, активизация употребления наиболее часто встречающихся префиксов и суффиксов, повторение видовременных форм английского глагола, ознакомление с правилами перевода повелительных предложений, встречающихся при работе с компьютером, перевод предложений с английского языка на русский.
Формы контроля: перевод слов и предложений, упражнения на закрепление грамматического материала (множественный выбор).
Оборудование: компьютер
Commands
Vocabulary
1) Let's switch on our computers. Look at the main Window commands.
1) Read the rules.
Префикс re имеет значение возобновления или повторения действия.
Префикс un имеет значение отрицания.
Суффиксы or, er указывают на принадлежность слова к существительному и имеют значение: 1) человек, выполняющий определенные действия; 2) инструмент, прибор, с помощью которого можно выполнить определенные действия.
Суффикс -tion указывает на принадлежность слова к существительному и имеет значение процесса выполнения какого-либо действия.
2) Translate the words
retry
recover
re-insert
rename
replace
unable
unlock
unpack
unrecoverable
unsuitable
printer
driver
computer
programmer
operator
commander
error
user
specification
destination
communication
creation
3) Find the sentences where Passive Voice, Present, Past or Future Tenses are used. Find imperative sentences. Translate the sentences.
1. Files in target drive will be erased.
2. Diskette is write protected.
3. Data on disk will be lost.
4. Write not completed.
5. No differences encountered.
6. Path not found.
7. No space left on device.
8. Last file was not backed up.
9. Graphics characters already loaded.
10. Make sure a diskette is inserted into the drive.
11. Not found.
12. Copy not completed.
13. Files in the target drive will be erased.
14. Press any key.
15. File does not exist.
16. Insert the first floppy disc in drive A and strike any key.
17. Disc unsuitable.
18. Disc full.
19. Check disc.
20. Press any key to begin recovery of the file on drive.
21. Restore the sequence.
22. Too many files open.
23. Copy complete.
24. Line too long.
25. Disc unsuitable for system disc.
26. Target disc is non-removable.
27. Error in file.
28. File creation error.
29. Incorrect number of parameters.
30. Do you wish to continue? Y/N
31. Warning.
32. Are you sure? Y/N
ТЕМА № 9. The Internet
Лексический материал: WWW - World Wide Web, to retrieve, network, to share, humanities, business transactions, access, to browse, browser, to provide, provider, broadcast live, site, to link, hyperlink, e-mail, to e-mail, to surf the net, search.
Грамматический материал: образование слов с помощь суффиксов (Word-building)
Формы проведения: ознакомление с новой лексикой и активизация употребления лексики по теме, ознакомление с компьютерным сленгом, чтение текста с пониманием основного и общего содержания, его обсуждение, короткие высказывания обучающихся. аудирование диалога и составление диалога, повторение грамматического материала, написание коротких сообщений с использованием компьютерного сленга, перевод предложений с русского языка на английский язык, самостоятельный поиск информации в Интернете, ознакомление с электронными словарями, использование электронной почты
Формы контроля: контроль аудирования диалога с помощью упражнения - множественный выбор, контроль навыков устной речи (диалог) и письменной речи (электронное письмо), упражнения на закрепление новой лексики и грамматики (тесты), контроль понимания текста с помощью различных упражнений.
Оборудование: компьютер
Урок 1.
The Internet
Warm up
1) Why do we use the Internet?
Listening
1) Listen to the dialogue and find the right variant. Work individually. (Приложение 2)
Questions:
1 .
Why did the net begin for?
.
Why did the net begin for?
a. for military reasons
b. for scientific reasons
c. for business
2. What year did it start in ?
a. 1959
b. 1969
c. 1979
3. When did people start calling it the ''Internet''?
a. the 1980s
b. the early 1990s
c. the late 1990s
4. When did the Internet start to grow very fast?
a. the late 1980s
b. the mid 1990s
c. the late 1990s
Vocabulary
1) Learn the new words.
-
WWW (World Wide Web) - «Всемирная паутина»
-
to retrieve- извлекать
-
network - сеть
-
to share - делить
-
humanities - гуманитарные науки
-
business transactions - коммерческие операции
-
access - доступ
-
to browse - рассматривать, разглядывать
-
browser - браузер (программа поиска информации)
-
to provide - обеспечивать (чем-либо)
-
provider - провайдер (компания, предоставляющая доступ к WWW через местные телефонные сети)
-
broadcast live - передавать в прямом эфире
-
site - сайт, страница
-
t
 o
link - соединять
o
link - соединять
-
hyperlink - гиперссылка
-
e-mail - электронная почта
-
to e-mail - посылать по электронной почте
-
to surf the net- путешествовать по Интернету
-
search - поиск
Reading
1) Read the text.
INTRODUCTION ТО THE WWW AND THE INTERNET
Millions of people around the world use the Internet to search for and retrieve information on all sorts of topics in a wide variety of areas including the arts, business, government, humanities, news, politics and recreation. People communicate through electronic mail (e-mail), discussion groups, chat channels and other means of informational exchange. They share information and make commercial and business transactions. All this activity is possible because tens of thousands of networks are connected to the Internet and exchange information in the same basic ways.
The World Wide Web (WWW) is a part of the Internet. But it's not a collection of networks. Rather, it is information that is connected or linked together like a web. You access this information through one interface or tool called a Web browser. The number of resources and services that are part of the World Wide Web is growing extremely fast. In 1996 there were more than 20 million users of the WWW. People connected to the Internet and World Wide Web through the local providers have access to a variety of information. Each browser provides a graphical interface. You move from place to place, from site to site on the Web by using a mouse to click on a portion of text, icon or region of a map. These items are called hyperlinks or links. Each link you select represents a document, an image, a video clip or an audio file somewhere on the Internet. The user doesn't need to know where it is, the browser follows the link.
All sorts of things are available on the WWW. One can use the Internet for recreational purposes. Many TV and radio stations broadcast live on the WWW. You can even visit museums, gardens, cities throughout the world, learn foreign languages and meet new friends. And, of course, you can play computer games through WWW, competing with partners from other countries and continents.
2) Answer the questions
1. What is the Internet used for?
2. What is the World Wide Web?
3. What is Web browser?
4. What does a user need to have an access to the WWW?
5. What are hyperlinks?
6. What resources are available on the WWW?
7. What are the basic recreational applications of the WWW?
3) Give the definition to the following terms.
1. The Internet
2. The World Wide Web
3. Web browser
4. Internet provider :
5. Hyperlinks
4) Complete the sentences with the following words: web browser, providers, link, WWW
1. You access the information through one interface or tool called a ...
2. People connected to the WWW through the local ... have access to a variety of information.
3. The user doesn't need to know where the site is, the ... follows the ...
4. In 1996 there were more than 20 million users of the ...
5. Each ... provides a graphical interface.
6. Local.. .charge money for their services to access ... resources.
5) Which sentences are true and which are false?
1. There are still not so many users of the Internet.
2. There is information on all sorts of topics on the Internet, including education and weather forecasts.
3. People can communicate through e-mail and chat programs only.
4. The Internet is tens of thousands of networks which exchange the information in the same basic way.
5. You can access information available on the World Wide Web through the Web browser.
6. You need a computer (hardware) and a special program (software) to be a WWW user.
7. You move from site by clicking on a portion of text only.
8. Every time the user wants to move somewhere on the Web he (she) needs to step by step enter links and addresses.
9. Films and pictures are not available on the Internet.
10. Radio and TV- broadcasting is a future of the Internet. They are not available yet.
Talking
What is the Internet? Why do we use it? Is the Internet important in our life? Is it harmful? Do you use the Internet? Discuss it with your partner.
Writing
Translate the text from Russian into English.
Одно из самых важных функций, которые компьютеры выполняют для людей, помогают общаться. Общение состоит в том, как люди обмениваются информацией. Компьютеры помогли людям достичь высот в науке, медицине, бизнесе, и изучении, потому что они позволяют специалистам во всем мире делиться информацией. Они также позволяют людям общаться друг с другом, поделитесь их мнениями, найти необходимую информацию. Интернет позволяет людям общаться между их компьютерами.
Блоги используются многими людьми, чтобы сказать, с какой целью они используют Интернет. Некоторые люди проводят большую часть своего времени, читая и сочиняя блоги. Много людей со всех континентов используют их. Некоторые люди используют их, чтобы написать о том, что с ними случилось. Специалисты могут использовать их, чтобы помочь людям учиться. Некоторые блоги используются компаниями, чтобы продать свой товар.
Урок 2. The Internet
Warm up
1) Have you surfed the net today?
2) For what purpose have you used the Internet?
Vocabulary
1) Match the definition with the correct spelling word.1. A place on the Internet that gives you information about a particular subject or product
2. An international network of computers
3. The system that stores information for computer users around the world
4. A system that allows massages to be sent from one computer to another
a. E-mail
b. the Internet
c. web site
d. World Web Site
2) Read the list of words to write an e-mail.
RL - real life cu - see you
lol - laugh out loud tia - thanks in advance
bbl - be back later ty - thank you
n2m - not too much 18er - later
BTW - by the way net potato - someone who spends much
SYS - see you soon time surfing the net
IMHO - in my humble opinion newbie - a new user of the Internet
LY - love you *puter - computer
4u - for you :-) - smile
wuzup - what's up? :-( - crying
F2F - face to face :-O - shocked
ASAP - as soon as possible
Write an e-mail to your friend. If you know some other words, you can use them.
Grammar
Fill in the gaps using the right form of the words: invent, science, growth, favor, friend, actual
The Pros and Cons of the Internet.
The Internet is without doubt one of the most important _____(1) in history. It was started in 1968 by the US but at first it was used mainly by______(2). Since 1990, when the World Wide Web was created, it has changed the world and its uses are______ (3) every day. You can use the Internet to read newspapers and magazines, play games, plan your holiday or buy from your _______ (4) shop. E-mail makes it possible to send electronic messages anywhere in the world in seconds, and you use Internet to "chat" with people and make new friends. As for Internet________(5), sitting at home in front of a computer making "chat friends" is not the same as______(6) meeting people.
Reading
Read and translate the instruction. Follow it.
Question: How сan you find the information in the
Internet?
The answer: in different cases it is necessary to operate
differently.
The common recommendations are:
-
Work at once with several search Nets or use special catalogues.
-
It is necessary to begin search using short information: one - two words.
-
Remember an old aphorism: "In the Internet it is possible to find any information, but concrete information you will not find ".
So give a concrete information, and your information will find you independently.
Practical work
Find On Line dictionaries. You can use the following information.
lingvo.ru
multilex.mail.ru
slovary.yandex.ru
rambler.ru/dict/
ТЕМА № 10. Express yourself
Формы проведения: поиск информации в Интернете, работа над проектами, защита проектов, подведение итогов.
Формы контроля: обсуждение проектов.
Оборудование: компьютер
We will spend some time at a computer class to learn more about the computers. Use any search engine www.yahoo.com,, www.lycos.com, www.infoseek.com. Each student type in anything that interests him or her particularly in connection with the computers. It can be terms, like the word computer, or chip, or hacker; it can be people, like Charles Babbage, Bill Gates. They can take notes and then make short presentations to the whole class.
ТЕМА № 11. Check your progress
Формы проведения: контрольная работа
Формы контроля: проверка тестовых заданий, комментарии.
Check your Progress.
-
Listen to the following definitions and choose computing terms. (Приложение 3)
a. disc, b. monitor, c. mouse, d. file, e. hardware, f. E-mail, g. WWW
II. Match the definition with the correct spelling word.
2. memory
3. input
4. output
5. processor
6. bit
7. chip
8. Internet
9. printer
10. cursors
a) information or instructions put into a computer
b) device that prints, especially one operated by a computer
c) the basic unit of information in an electronic computer, equivalent to a choice between two possibilities, such as "yes" or "no"
d) an electronic machine that can store, recall, or process information
e) information put out by or delivered by a computer
f) an extremely large computer network, including many smaller networks of university, government, business, and private computers, linked by telephone lines
g) a movable mark on a computer display screen, indicating the point at which the displayed data may be altered or processed, or at which new data may be inserted
h) system of storing information in a computer on magnetic tape; storage
i) a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon, which holds an integrated circuit
j) the central processing unit of a computer, especially the part of this unit in which data are examined, compared, changed, etc.
III. Using words from the list, fill in the blanks with the correct answers: a. computer(s), b. operator(s), c. printer(s), d. build, e. design, f. information, g. type(s), h. programmer(s), i. machine
1. A computer is a _____ that stores _____ for later use and
processes that _____ on demand.
2. Those who _____ and _____ new systems of computers are _____
.
3. Most people working with computers are either _____ or _____
.
4. A computer operator is the one who actually runs a _____ .
5. The operator uses the machine to prepare reports, ____,
changes paper in the _____ .
6. The computer programmer is the person who tells the _____ how
work.
IV. Many people think computers are too expensive and just a waste of money. Do you know why they are so expensive? Read the passage and find the answer to this question.
Mike Aghopian (California, USA):
I work for ICM, a computer company in California.
As you probably know, the chip is the brain of the computer, the most important part. Why does it have to be small? Well, there are two reasons. Number one is convenience: we want nice, small, portable machines. Number two is speed: in a small circuit the electronic signals arrive faster, simply because they travel a shorter distance.
Today's chips are very small indeed. But we design the electronic circuit on big pieces of paper. Then we make a big photographic negative - as big as a table. Finally we print this picture on a piece of silicon 250 times smaller than the negative. That's the secret of making chips!
W e
cut the pieces of silicon under a microscope. Then we test the
chips. Only 30% work correctly, so we throw away about 70%.
That's why they are expensive.
e
cut the pieces of silicon under a microscope. Then we test the
chips. Only 30% work correctly, so we throw away about 70%.
That's why they are expensive.
A modern chip can store more than 8 million characters - that's 4,000 pages of a book!
Read the text again and draw a flow-chat to show how chips are made. Use these phrases:
-
sell the good one
-
cut the silicon
-
test the chips
-
design on paper
-
photographic negative
-
throw away the bad ones
-
print on silicon
Заключение
При реализации данной программы предполагается использовать различные методы и приемы обучения. Предъявление материала осуществляется с помощью объяснения, ознакомления с новой лексикой, аудирования текстов по данной теме, чтения текстов с извлечением необходимой информации и с полным пониманием различных типов текстов, в том числе и технических. Закрепление и проверка понимания освоения нового материала проводится с помощью словарной работы, моделирования ситуации, проектной деятельности, презентации, обсуждения, письменной работы и различных лексических и грамматических упражнений типа: ответить на вопросы, «правильно-неправильно», закончить предложения, множественный выбор, перевести, соотнести.
Формами контроля могут быть: устные ответы на каждом уроке, различные упражнения на закрепление лексического и грамматического материала (тесты), упражнения по тексту с целью извлечения полной или необходимой информации, письменные работы, монологические и диалогические высказывания, перевод предложений с английского языка на русский язык и перевод предложений с русского языка на английский язык, проектная работа.
В процессе обучения учащиеся приобретают следующие конкретные умения:
Коммуникативные умения:
-
понимать звучащую англоязычную речь;
-
запрашивать необходимую информацию;
-
адекватно реагировать на реплики и поддерживать беседу;
-
аргументировано отстаивать свою точку зрения, находить компромисс;
-
лаконично высказываться.
Интеллектуальные умения:
-
умение работать с информацией и с текстом;
-
выделять главную мысль и анализировать информацию;
-
делать обобщения и выводы;
-
писать изложение и выражать свое мнение.
Практические умения:
-
использовать компьютерные и Интернет технологии.
Материально-техническое обеспечение работы с пособием предполагает использование: компьютера, проектора, ресурсов сети Интернет. На занятиях планируется использовать раздаточный материал для учащихся: тексты по предлагаемым темам, грамматические упражнения с целью повторения грамматического материала, лексически упражнения для закрепления и активизации употребления новых лексических единиц, в том числе и специальных терминов, тестовые задания
Список использованной литературы и ресурсов Интернет
-
Агабекян И. П. Английский язык для ссузов. Учебное пособие. - " Издательство" Проспект", 2014.
-
Английский язык: Сборник текстов и упражнений для студентов I - II курсов. Сост. Р.Б. Галимулина. - Йошкар- Ола: МарГТУ, 2013. - 84с
-
. Гроза О.Л. и др. New Millennium English 10. Учебник английского языка для 10 класса общеобразовательных учреждений. Титул, 2014.
-
Моделирование и конструирование урока в контексте требований ФГОС Анализ урока в контексте реализации ФГОС общего образования // Справочник заместителя директора школы. - 2014. - №11. - С. 99 - 102.
-
Полякова Т.Ю. Английский язык для диалога с компьютером: Учебное пособие для технических вузов. М. Высшая школа, 2012.
-
Щербакова И. В. Особенности обучения грамматике английского языка в неязыковых вузах //European science. - 2015. - №. 4 (5).
-
Ресурсы Интернет:
festival.1september.ru - Фестиваль открытых уроков,
www. fio.ru - Федерация Интернет образования.
Приложение 1
Тема 3.
Listening
- Hi, Mark.
- Hi, Helen .How are you?
- Fine thanks .I need your help Mark. What's the problem?
- I have problems with my computer and I know you are very good at solving them. Yesterday I was writing my essay for tomorrow's lesson and suddenly my computer crashed and I lost all my work! Do you think it is possible to get it back?
- Did you make a back-up copy of your work? - I'm afraid I forgot.
- I'm sorry, Helen, but I can't see any way of getting your essay back. Remember you always have to make a back-up copy of your work.
- I know, but I always forget about it.
- Do you use a computer a lot at school?
- I write all my essay and exercises on the computer but I think mine is not user-friendly. Moreover, it has become obsolete and I have to replace it.
- That's true, technology advances so fast that the computer, which I bought last year, is already old-fashioned.
- Do you have access to the Internet at home?
- Yes, I do .I send e-mails to my friends around the world .Do you often use the Internet?
- I have access to the Internet at school and I often surf the net to find some information that I need for my work .I must admit it is very absorbing and I can sometimes spend hours on the Internet.
- That's true .You can forget about the whole world while using a computer and the Internet.
- All right, I have to go and write a new essay. This time I won't forget to make an extra copy on a floppy disk .See you later!
- Bye!
Приложение 2
Тема 9.
Listening
The History of the Internet.
Presenter: Welcome to ''Future Now'. Today we are going to discuss the Internet with Dr .Jennifer May from Manchester University. Dr .May, how did the Internet begin?
Dr. May: Well, it's strange but the Internet was started by the military. In the 1960s the Pentagon were worried about communications after a nuclear war. And in 1969 they thought of linking computers into a network so that if one part of the network was destroyed, other parts could continue working.
Presenter: And then scientists started to use the network, right?
Dr .May: Yes, people in universities all over the world began to use the network to share ideas .They used it for work and for fun. In the 1980s, people started calling it the Internet.
Presenter: Then it was in the mid-1990s that the Internet really began to grow fast.
Dr .May: Yes, now the Internet is important for entertainment, e-mail, playing games and getting information.
Приложение 3
Тема 11.
Listening
1. An input device that is moved around the desk top to control the position of the cursor on the display screen.
2. A television like screen to receive information from the computer.
3. Information or instructions which a computer keeps together under a single name.
4. The system that stores information for computer users around the world
5. The computer's machinery - the parts you can see and touch, like the monitor and all the electronic devices and circuits inside it.
6. An object like a phonograph record, made of metal or plastic and with a magnetic surface, used to store information and instructions for computer.
7. A system that allows massages to be sent from one computer to another
Приложение 4
-
2. апгрейд
7. представлять
8. сканер
10. принтер
11. цифровой
13. влиять
14. соединять
16. манера, способ
17. клавиатура
19. восстановить
20. иконки
1. цель
3. данные
4. инструкция
5. оружие
6. оборудование
9. обеспечивать
12. извлекать
14. зависать
15. выполнять
18. различный
21. курсор
1. цель
3. цифровой
4. данные
6. представлять
7. сканер
11. восстановить
13. монитор
15. мозг
16. выполнять
19. манера, способ
20. курсор
22. зависать
25. диск
26. различный
27. устройство
2. апгрейд, улучшение
5. файлы
8. управлять
9. клавиатура
10. принтер
12. извлекать
14.модем
17. соединять
18. иконки
21. достигать
23. оборудование
24. графический
1. различный
3. извлекать
6. мозг
9. сканер
10. принтер
11. графический
12. выполнять
15. инструмент
19. зависать
21. монитор
23. принимать
24. представлять
27. достигать
2. влиять
4. иконки
5. оружие
7. данные
8. управлять
13. курсор
14. диск
16. файлы
17. оборудование
18. числовой
20. сравнивать
22. восстановить
25. соединять
26. цель
Ключи к заданиям
Тема 1.
Урок 1. Grammar.
1. am helping; 2. plays; 3. am looking for; 4. uses; 5. opens; 6. are repairing; 7. are increasing.
Урок 2. Grammar.
Тема 2.
Grammar.
1. are buying; 2. works; 3. is holding; 4. doesn't leave; 5. are always talking; 6. am not teaching; 7. Do amphibians live; 8. never go; 9. prefer; 10. are having.
Тема 3.
Урок 1. Vocabulary.
4) software: program, instruction, symbol, results on the monitor, cursor, memory, process data.
hardware: mouse pad, mouse, printer, information, scanner, keyboard, modem, CPU.
5) 1 - d; 2 - a; 3 - c; 4 - b; 5 - e.
Урок 2. Vocabulary.
2) CD-ROM, loudspeaker, floppy disk, keyboard, mouse pad, input, database, hardware.
3) 1 - i; 2 - d; 3 - h; 4 - e; 5 - g; 6 - k; 7 - j; 8 - c; 9 - a; 10 - b; 11 - f
Тема 4.
Vocabulary.
1 - f; 2 - e; 3 - i; 4 - h; 5 - g; 6 - a; 7 - b; 8 - d; 9 - c.
Reading.
1 - F; 2 - T; 3 - F; 4 - NM; 5 - T; 6 - NM.
Тема 5.
Vocabulary.
1 - c; 2 - b; 3 - b; 4 - a; 5 - c.
Grammar.
3) 1 - d; 2 - f; 3 -j; 4 - c; 5 - i; 6 - b; 7 - h; 8 - e; 9 - a; 10 - g.
Тема 6.
Vocabulary.
1) BKSP - 6, e; CAPS LOCK - 5, b; PG UP - 4, c; PRT SC - 3, f;
NUM LOCK - 2, a; PG DN - 1, d.
2) 1 - enter; 2 - shift; 3 - home; 4 - break; 5 - end.3) DEL - c; INS - c; TAB - b; SHIFT - b.
Тема 7.Grammar.
1 - c; 2 - d; 3 - c; 4 - a; 5 - a.
Тема 8.
Grammar.
3)
1. Files in target drive will be erased.2. Diskette is write protected.
3. Data on disk will be lost.
4. Write not completed.
5. No differences encountered.
6. Path not found.
7. No space left on device.
8. Last file was not backed up.
9. Graphics characters already loaded
10. Make sure a diskette is inserted into the drive.
11. Not found.
12. Copy not completed.
13. Files in the target drive will be erased.
14. Press any key.
15. File does not exist.
16. Insert the first floppy disc in drive A and strike any key.
17. Disc unsuitable.
18. Disc full.
19. Check disc.
20. Press any key to begin recovery of the file on drive.
21. Restore the sequence.
22. Too many files open.
23. Copy complete.
24. Line too long.
25. Disc unsuitable for system disc.
26. Target disc is non-removable.
27. Error in file.
28. File creation error.
29. Incorrect number of parameters.
30. Do you wish to continue? Y/N
31. Warning.
32. Are you sure? Y/N
Файлы на дискете, на которую ведется запись будут уничтожены.
Дискета защищена от записи
Данные на диске будут потеряны
Запись не закончена
Не обнаружено различий
Путь к файлу не обнаружен
На устройстве (диске) не осталось места
Последний файл не был включен в резервную копию.
Графические символы уже загружены.
Убедитесь, что дискета вставлена в дисковод.
Не обнаружено.
Копирование не завершено.
Файлы в дисководе, на который ведется копированиe, будут стерты.
Нажми любую клавишу.
Такого файла не существует.
Вставьте первую дискетку в дисковод А и нажмите любую клавишу.
Диск неподходящий.
Диск переполнен.
Проверьте диск.
Нажмите любую клавишу для того, чтобы начать восстановление файлов на дисководе.
Открыто слишком много файлов.
Копирование завершено.
Строка слишком длинная.
Диск не подходит для системного диска.
Диск на который ведется копирование, является несъемным.
Ошибка в файле.
Ошибка при создании файла.
Неверное количество параметров.
Вы хотите продолжить? Да/Нет.
Предупреждение.
Вы уверены? Да/Нет.
Тема 9.
Урок 1. Listening.
1 - a; 2 - b; 3 - a; 4 - b.
Writing
One of the most important jobs that computers do for people is helping with communication. Communication is how people share information. Computers have helped people move forward in science, medicine, business, and learning, because they let experts from anywhere in the world work with each other and share information. They also let other people communicate with each other, do their jobs almost anywhere, learn about almost anything, or share their opinions with each other. The Internet is the thing that lets people communicate between their computers.
Blogs are used by many people to say what they want on the Internet. Some people spend most of their time reading and writing blogs. Many people</</font> from all over the world use them. Some people use them to write about things that happen to them. Experts can use them to help people learn more. Some blogs are used by companies to sell things.
Урок 2. Vocabulary.
1 - c; 2 - b; 3 - d; 4 - a.
Grammar.
1 - invention; 2 - scientists; 3 - grown; 4 - favourite; 5 - friends; 6 - actually.
Тема 10.
I. 1 - c; 2 - b; 3 - d; 4 - g; 5 - e; 6 - a; 7 - f.
II. 1 - d; 2 - h; 3 - a; 4 - e; 5 - j; 6 - c; 7 - i; 8 - f; 9 - b; 10 - g.
III. 1 - machine; information; information.
2 - build; design; programmers.
3. operators; programmers.
4. computer.
5. types; printers.
6. computer.
Согласовано:
на заседании ПЦК
«Гуманитарного цикла»
Протокол № 5
от « » января 2016 г.
Председатель ПЦК
__________________В.В. Дмитриева