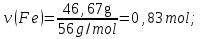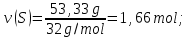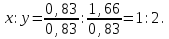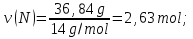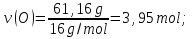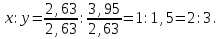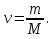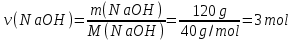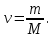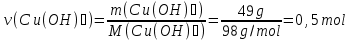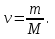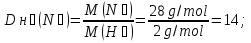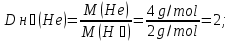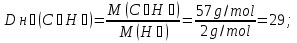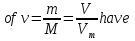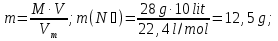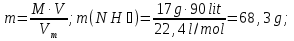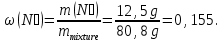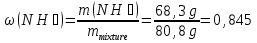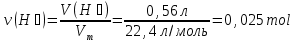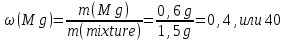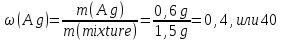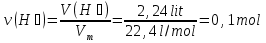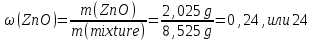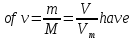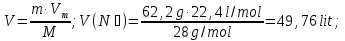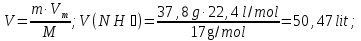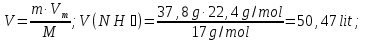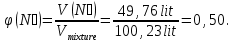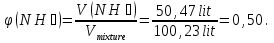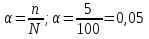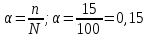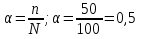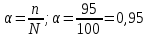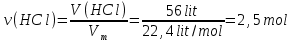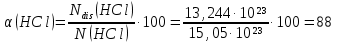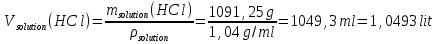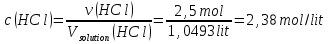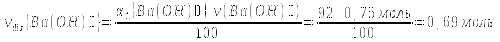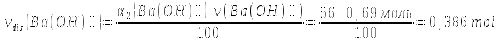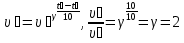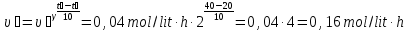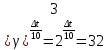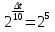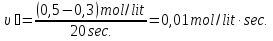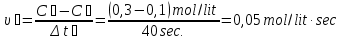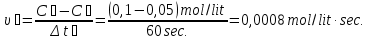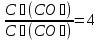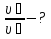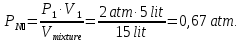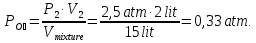- Учителю
- Решение задач по химии
Решение задач по химии
Finding the relative molecular mass of the substance .
-
Find the molar mass of aluminum sulfate . Indicate the relative molecular weight of the substance.
given:
АІ2(SО4)3
find:
М[АІ2(SО4)3] -?
Мr[АІ2(SО4)3] -?
Solution:
М[АІ2(SО4)3] = А(АІ) · n(АІ) + А(S) · n(S) + А(О) · n(О)
М[АІ2(SО4)3] = 27 · 2 + (32 + 16 · 4) · 2 = 54 + 96 · 3 =
= 54 + 288 = 342 g/mol
Мr[АІ2(SО4)3] = Аr(АІ) · n(АІ) + Аr(S) · n(S) + Аr(О) · n(О)
Мr[АІ2(SО4)3] = 27 · 2 + (32 + 16 · 4) · 2 = 54 + 96 · 3 =
= 54 + 288 = 342 .
Answer: М[АІ2(SО4)3] = 342 g/mol; Мr[АІ2(SО4)3] = 342.
-
Find the molar mass of phosphoric acid. Indicate the relative molecular weight of the substance.
given:
Н3РО4
find:
М(Н3РО4) -?
Мr(Н3РО4) -?
Solution:
М(Н3РО4) = А(Н) · n(Н) + А(Р) · n(Р) + А(О) · n(О)
М(Н3РО4) = 1 · 2 + 31· 1 + 16 · 4 = 2 + 31 + 64 = 98 g/mol
Мr(Н3РО4) = Аr(Н) · n(Н) + Аr(Р) · n(Р) + Аr(О) · n(О)
Мr(Н3РО4) = 1 · 2 + 31· 1 + 16 · 4 = 2 + 31 + 64 = 98
Answer: М(Н3РО4) = 98 g/mol; Мr(Н3РО4) = 98.
Calculations by chemical formulas.
-
What is the mass attitude of elements in substances the formula which SO3?
given:
SO3
find:
m (S): m (O)
Solution:
Mr(SO3) = Ar(S)+ 3Ar(O) = 32 + 3 · 16 = 80
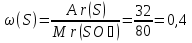
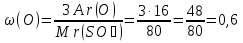
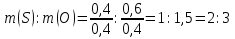
Answer: m(S) : m(О) = 2 : 3.
-
What is the mass attitude of elements in substances the formula which CuO?
given:
CuO
find:
m(Cu) : m(О)
Solution:
Мr(CuO) = Аr(Cu) + Аr(O) = 64 + 16 = 80
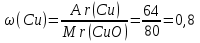
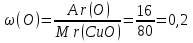
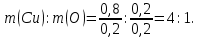
Answer :m(Cu) : m(О) = 4 : 1.
Of the mass fraction of the chemical element in the compound .
-
Calculate the mass fraction of each element in marble , whose composition corresponds to the formula CaCO3.
given:
CaCO3
find:
ω(Ca) - ?
ω(C) -?
ω(O) -?
Solution:
Мr(CaCO3) = Аr(Ca) + Аr(C) + 3Аr(O) = 40 + 12 + 3 · 16 = 100
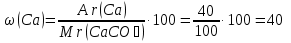
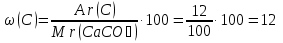
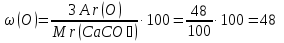
Answer :ω(Ca) = 40 %; ω(C) = 12 %; ω(O) = 48 %.
-
What is the mass fraction of oxygen in the compound whose formula Al2O3?
given:
Al2O3
find:
ω(O) -?
Solution:
Мr(Al2O3) = 2Аr(Al) + 3Аr(O) = 2 · 27 + 3 · 16 = 102
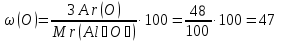
Answer : ω(O) = 47 %.
-
Calculate the mass fraction of each element in the magnesium sulphate MgSO4
given:
MgSO4
find:
ω(Mg) - ?
ω(S) -?
ω(O) -?
Solution:
Мr(MgSO4) = Аr(Mg) + Аr(S) + 4Аr(O) = 24 + 32 + 4 · 16 = 120
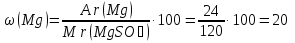
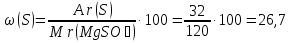
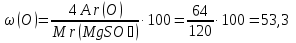
Answer:ω(Mg) = 20 %; ω(S) = 26,7 %; ω(O) = 53,3 %.
Derivation of the formulas of compounds .
-
Mass fractions of iron and sulfur of compounds are, respectively, 46.67% and 53.33 %.Determine the formula of this compound.
given:
ω(Fе) = 46,67 %
ω(S) = 53,33 %
find :
Fех Sу -?
Solution:
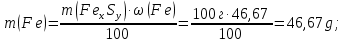
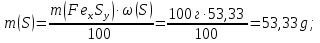
М(Fе) = 56 g/mol,
М(S) = 32 g/mol,
ν(Fе) : ν(S) = х : у = 0,83 : 1,66
formula iron compound FеS2.
Answer: FеS2.
-
Mass fraction of nitrogen in the of oxide nitrogen equal to 36.84 %. Output the simplest formula this of oxide .
given:
ω(N) = 36,84 %
find :
NхОу -?
Solution:
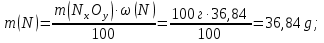
m(О) = m(NхОу) - m(N) = 100 g -36,84 g = 61,16 g
М(N) = 14 g/mol,
М(О) = 16 g/mol,
ν(N) : ν(О) = х : у = 2,63 : 3,95
simplest formula oxide N2О3.
Answer: N2О3.
Major quantitative characteristics substances: a substance amount , mass, volume and number of molecules.
-
Calculate the amount of a substance that is 120 g of sodium hydroxide.
given:
m(NаОН) = 120 g
find:
ν(NаОН) - ?
Solution:
М(NаОН) = 23 + 16 + 1 = 40 g/ mol
Answer:ν(NаОН) =3 mol.
-
Calculate the amount of substance which corresponds to 49 g of copper hydroxide (II).
given:
m(Сu(ОН)2) = 49 g
find:
ν(Сu(ОН)2) - ?
Solution:
М(Сu(ОН)2) = 64 + 16 · 2 + 1 · 2 = 98 g/mol
Answer:ν(Сu(ОН)2) =0,5 mol.
-
Calculate the amount of substance corresponding to 490 g of sulfuric acid, H2SO4 .
given:
m(Н2SО4) = 490 г
Найти:
ν(Н2SО4) - ?
Решение:
М(Н2SО4) = 1· 2 + 32 + 16 · 4 = 98 г/моль
Ответ: ν(Н2SО4) =.5 моль.
-
Calculate the amount of substance corresponding to 9.8 g phosphoric acid H3PO4 .
given:
m(Н3РО4) = 9,8 г
Найти:
ν(Н3РО4) - ?
Решение:
М(Н3РО4) = 1· 3 + 31 + 16 · 4 = 98 г/моль
Ответ: ν(Н3РО4) =.0,1 моль.
-
Equal amounts of whether the substance contains 4 g of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas of 64 g ?
given:
m(Н2) = 4 g
m(О2) = 64 g
find:
ν(Н2) - ?
ν(О2) - ?
Solution:
1- way:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
4 g Н2 ----- х mol Н2
2 g Н2 ----- 1 mol Н2
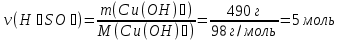
2- way:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
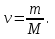
1- way:
М(О2) = 32 g/mol
64 g О2 ----- х mol О2
32 g О2 ----- 1 mol О2
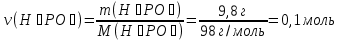
2- way:
М(О2) = 32 g/mol
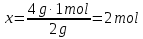
Answer: ν(Н2) = 2 mol; ν(О2) = 2 mol - Identical.
-
Identical to the number of substances contained in water, 18 and 17 g H2S?
given:
m(Н2О) = 18 g
m(H2S) = 17 g
find:
ν(Н2О) - ?
ν(H2S) - ?
Solution:
1- way:
М(Н2О) = 18 g/mol
18 g Н2О ----- х mol Н2О
18 g Н2О ----- 1 mol Н2О
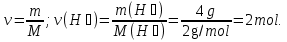
2- way:
М(Н2О) = 18 g/mol
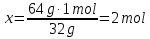
1- way:
М(H2S) = 34 g/mol
17g H2S ----- х mol H2S
34 g H2S ----- 1 mol H2S
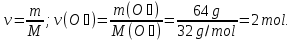
2- way:
М(H2S) = 34 g/mol
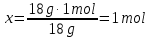
Answer:ν(Н2О) = 1 mol; ν(H2S) = 0,5 mol - Misc.
-
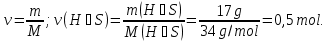
Identical do the amount of the substance contained in 44 g of CO2 and
2 g of hydrogen H2?
given:
m(СО2) = 44 g
m(Н2) = 4 g
find:
ν( СО2) - ?
ν(Н2) - ?
Solution:
1- way:
М(СО2) = 44 g/mol
44 g СО2 ----- х mol СО2
44 g СО2 ----- 1 mol СО2
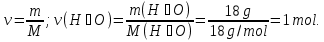
2- way:
М(СО2) = 44 g/mol
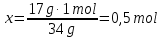
1- way:
М(Н2) =2 g/моль
2 g Н2 ----- х mol Н2
2 g Н2 ----- 1 mol Н2
2- way:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
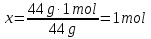
Answer:ν(СО2) = 1 mol; ν(Н2) = 1 mol-Identical.
-
What proportion of moles are 9 grams of water ?
given:
m(Н2О) = 9 g
find:
ν(Н2О) - ?
Solution:
1- way:
М(Н2О) = 18 g/mol
9 g Н2О ----- х mol Н2О
18 g Н2О ----- 1 mol Н2О
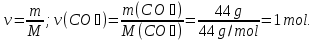
2- way:
М(Н2О) = 18 g/mol
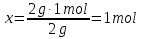
Ответ: ν(Н2О) = 0,5 mol.
-
What proportion of moles is 1 g of hydrogen H2?
given:
m(Н2) = 1 g
find:
ν(Н2) - ?
Solution:
1- way:
М(Н2) =2 g/mol
1 g Н2 ----- х mol Н2
2 g Н2 ----- 1 mol Н2
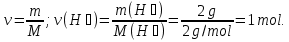
2- way:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
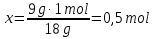
Answer: ν(Н2) = 0,5 mol.
-
What proportion of mole are 71 g of sodium sulfate Na2SO4?
given:
m(Na2SO4) = 71 g
find:
ν(Na2SO4) - ?
Solution:
1- way:
М(Na2SO4) = 142 g/mol
71 g Na2SO4 ----- х mol Na2SO4
142 g Na2SO4 ----- 1 mol Na2SO4
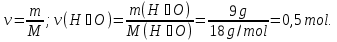
2- way:
М(Na2SO4) = 2 g/mol
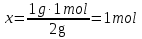
Answer:ν(Na2SO4) = 0,5 mol.
The relative density of the gases.
-
Determine the relative density of nitrogen to hydrogen .
given:
М(N2) = 28 g/mol
find:
Dн₂(N2) -?
Solution:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
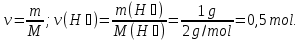
Answer:Dн₂(N2) = 14.
-
Determine the relative density of helium to hydrogen .
given:
М(Не) = 4 g/mol
find:
Dн₂(Не) -?
Solution:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
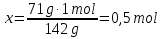
Answer:Dн₂( Не) = 2.
-
Determine the relative density of butane C4H9 hydrogen
given:
М(С4Н9) = 57 g/mol
find:
Dн₂(С4Н9) -?
Solution:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
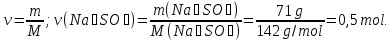
Answer:Dн₂(С4Н9) = 29.
Mass , volume fraction of the substance in the mixture.
-
Determine the weight fraction of nitrogen in the mixture thereof with ammonia , if the volume fraction of nitrogen in the mixture is 10%.
given:
φ(N2) = 10 %
find:
ω(N2) -?
Solution:
Vmixture = 100 lit
V(N2) = 10 lit, а V(NН3) = 100 lit - 10 lit= 90 lit
М(N2) = 28 g/mol
М(NН3) = 17 g/mol
Vm= 22,4 l/mol
mmixture = 12,5 g + 68,3g = 80,8 g
Answer:ω(N2) = 0,155.
-
The powder mixture of magnesium and silver weight 1,5 g treated with excess of a solution of sulfuric acid ,wherein stood 560 ml (normal conditions) of hydrogen . Calculate the mass ratio ( in percentage ) of the components in the initial mixturegiven:
given:
m(mixture) =1,5 g
V (Н2) = 560 ml
find:
ω(Мg) -?
ω(Аg) -?
Solution:
Мg + Н2SО4 = МgSО4 + Н2↑
Silver does not react :
Аg + Н2SО4(dil.) ↛
ν(Н2) = ν(Мg) ⇒ν(Мg) = 0,025 mol
М(Мg) = 24 g/mol
m(Мg) = ν(Мg) · М(Мg) = 0,025 mol · 24 g/mol = 0,6 g
m(Аg) = m(mixture) - m(Мg) = 1,5 g - 0,6 g = 0,9 g
Answer:ω(Мg) = 40 %; ω(Аg) = 40 %.
-
A mixture of zinc oxide and zinc weight 8,525 g was treated with excess hydrochloric acid, wherein stood 2,24 liters of gas (normal conditions ) .Calculate the weight fraction (in percent ) of zinc oxide in the initial mixture.
given:
m(mixture) = 8,525 g
V(Н2) = 2,24 lit
find:
ω(ZnО) -?
Solution:
ZnО + 2НСl = ZnСl2 + 2Н2О (1)
Zn + 2НСl = ZnСl2 + Н2↑ (2)
ν(Н2) = ν(Zn) ⇒ ν(Zn) 0,1 mol
М(Zn) = 65 g/mol
m(Zn) = ν(Zn) · М(Zn) = 0,1 mol · 65 g/mol = 6,5 g
m(ZnО) = m(mixture) - m(Zn) = 8,525 g - 6,5 g = 2,065 g
Answer:ω(ZnО) = 24 %.
-
Determine the volume fraction of nitrogen in the mixture thereof with ammonia , if the mass fraction of nitrogen in the mixture is 62,2 %.
given:
ω(N2) = 62,2 %
find:
φ(N2) -?
Solution:
mmixture = 100 g
m(N2) = 62,2 g, а m(NН3) = 100 g - 62,2 g = 37,8 g
М(N2) = 28 g/mol
М(NН3) = 17 g/mol
Vm= 22,4 l/mol
Vmixture = 49,76 lit + 50,47 lit = 100,23 lit
Answer:φ(N2) = 0,50.
-
Calculatevolume fractionhydrogen and helium in a mixturecontaining 20 %( by weight)hydrogen .
given:
ω(Н2) = 20 %
find:
φ(Н2 and Не) -?
Solution:
М(Н2) = 2 g/mol
m(Н2) = ν(Н2) · М(Н2) = 20 mol · 2 g/mol = 40 g
М(N2) = 28 g/mol
М(NН3) = 17 g/mol
Vm= 22,4 л/mol
V = 49,76 + 50,47 = 100,23 lit
Answer:φ(N2) = 0,50.
Electrolytic dissociation . Reactions in electrolyte solutions.
-
In the solution was placed of 100 molecules . Determine the degree of dissociation , if dissociated 5of molecules.
given:
n = 5 molecules
N = 100 molecules
find:
α -?
Solution:
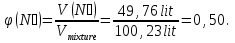
Answer:α = 0,05.
-
In the solution was placed 100 molecules .Determine the degree of dissociation , if dissociated 15 of molecules .
given:
n = 15 molecules
N = 100 molecules
find:
α -?
Solution:
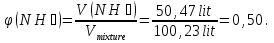
Answer:α = 0,15.
-
In the solution was placed 100 molecules .Determine the degree of dissociation , if dissociated 50 of molecules .
given:
n = 50 molecules
N = 100 molecules
find:
α -?
Solution:
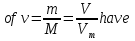
Answer:α = 0,5.
-
In the solution was placed 100 molecules .Determine the degree of dissociation , if dissociated 95 of molecules .
given:
n = 95 molecules
N = 100 molecules
find:
α -?
Solution:
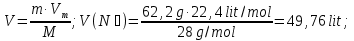
Answer:α = 0,95.
-
In 1 liter of water dissolved 56 l (under normal conditions) ofhydrogen chloride . In The resulting solution contains 13,244 · 1023 of chloride ions. Determine the molar concentration of and the degree of dissociation of the obtained hydrochloric acid, if the density of the resulting solution is 1 g/ml.
given:
V(Н2О) = 1 lit
V(НСl) = 56 lit
N(Сl-) = 13,244· 1023
ρsolution(НСl) = 1,04 g/ml
find:
α(НСl) -?
с(НСl) -?
Solution:
N(НСl) = ν(НСl) · NА = 2,5 mol · 6,02 · 1023 = 15,05 · 1023
НСl → Н+ + Сl-
N(Сl-) = Ndis(НСl) = 13,244· 1023
М(НСl) = 36,5 g/mol
m(НСl) = ν(НСl) · М(НСl) = 2,5 mol · 36,5 g/mol = 91,2 V(Н2О) · ρ(Н2О) = 1000 ml · 1 g/ml = 5 g.
m(Н2О) =1000 g.
msolution(НСl) = m(Н2О) + m(НСl) = 1000 g + 91,25 g = 1091,25 g.
Answer: ω(НСl) = 88 %; с(НСl) = 2,38 mol/lit.
-
The degree of dissociation of barium hydroxide on the first stage-92%, the second stage-56%. Calculate the number of cations barium and hydroxide ions in 0,5 liters 1,5 M solution.
given:
α1(Ва(ОН)2) = 92 %
α2(Ва(ОН)2) = 56 %
Vsolution(Ва(ОН)2) = 0,5 л = 500 ml
с(Ва(ОН)2) = 1,5 М = 1,5 mol/lit
find:
N(Ва2+) -?
N(ОН-) -?
Solution:
-
Ва(ОН)2 ⇄ Ва(ОН)+ + ОН-;
-
Ва(ОН)+⇄ Ва2+ + ОН-.
ν(Ва(ОН)2) = с(Ва(ОН)2) · Vsolution(Ва(ОН)2) = 1,5 mol/lit · 0,5 lit = 0,75 mol
ν(Ва(ОН)+) = ν1(ОН)- = νdis(Ва(ОН)2) = 0,69 mol
ν(Ва²+) = ν2(ОН)- = νdis(Ва(ОН)⁺) = 0,386 mol
N(Ва2+) = ν(Ва2+) · NА = 0,386 mol · 6,02 ·1023mol-1 = 2,324 ·1023
ν(ОН-) = ν1(ОН)- + ν2(ОН)- = 0,69 mol+ 0,386 mol = 1,076 mol
N(ОН-) = ν(ОН-) · NА = 1,076 mol · 6,02 ·1023mol-1 = 6,478 ·1023
Answer: N(Ва2+) = 2,324 ·1023; N(ОН-) = 6,478 ·1023.
The chemical reaction rate . Chemical equilibrium .
-
When the temperature rises at a rate of 100C chemical reaction increases two fold. When the 200C it is equal to 0,04 mol/(lit · h). What will be the rate of the reaction at 40 ° C?
given:
γ = 2
υ1 = 0,04 mol/lit· h
t1 = 200С
t2 = 400С
find:
υ2 -?
Solution:
Answer: υ2 = 0,16 mol/lit · h
-
When the temperature rises at a rate of 100C chemical reaction increases two fold. When the 200C it is equal to 0,04 mol/(lit · h). What will be the rate of the reaction at 10 ° C?
given:
γ = 2
υ1 = 0,04 mol/lit · h
t1 = 200С
t2 = 100С
find:
υ2 -?
Solution:
Answer: υ2 = 0,02 mol/lit · h
-
At temperature 20 ° C the reaction lasts 2 hours 40 minutes. At what the reaction stops end for 5 minutes if the temperature coefficient of the reaction of is 2 .
given:
γ = 2
τ1 = 2 h 40 min
τ2 = 5 min
t1 = 200С
find:
t2 -?
Solution:
Δt = t2 - t1
t2 = Δt + t1
1) τ1 = 2 h 40 min = 2 · 60 + 40 = 160 min
τ2 = 5 min
160 : 5 = 32 .
4) t2 = 50 + 20 = 70
Answer: at 700 ° C, the reaction is over in 5 minutes.
-
When the temperature rises at a rate of 100C chemical reaction increases two fold. When 200C it is equal to
0,04 mol/( lit · h). What will be the rate of the reaction at 0 ° C?
given:
γ = 2
υ1 = 0,04 mol/lit· h
t1 = 200С
t2 = 00С
find:
υ2 -?
Solution:
Answer: υ2 = 0,01 mol/lit · h
-
The reaction proceeds at a temperature of 500C for
3 min 20 s.The temperature coefficient of the reaction rate is equal to 3 .How much time will end this reaction at 300C .
given:
γ = 3
τ1 = 3 min 20 s
t1 = 500С
t2 = 300С
find:
τ2 -?
Solution:
τ inversely proportionalt0 С
In 9 times the rate of reaction will decrease as the temperature decreases from 500C to 300C
2) Time of course of the reaction at lower temperatures will increase by
9 times :200 sec · 9 = 1800 sec = 30 минут - за столько времени закончится эта реакция при понижении температуры с 500С до 300С.
Answer: at a temperature of 300 ° C for 30min the reaction stops.
-
Calculate of the average rate of the reaction : А + В = С, if after 10 seconds, the concentration of substance A was 0,2 mol/lit, and of after 40 seconds , the concentration of this substance was of 0,02 mol/lit.
given:
t1 = 10 sec
t2 = 40 sec
с1 = 0,2 mol/lit
с2 = 0,02 mol/lit
find:
υ - ?
Solution:
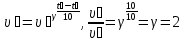
Answer: υ =0,06 mol/lit · sec.
-
20 seconds after the start of the reaction 2SО2 + О2 → 2SО3 3,2 g remain unoxidised of 4,8 g of sulfur oxide (IV). Find the rate of oxidation of sulfur dioxide .
given:
m1(SО2) = 4,8 g
m2(SО2) = 3,2 g
Δt = 20 sec
find:
υ - ?
Solution:
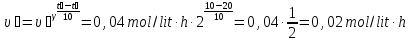
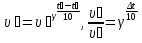
М(SО2) = 64 g/mol
if V = 1 lit, т.
Answer: υ =0,00125 mol/lit · sec.
-
The decomposition reaction HBr on simple substance proceeds in the vessel volume 2 liters.Initially, the in vessel containing the 0,5 mol/lit of hydrogen bromide , the after 20 seconds the amount substance was 0,3 mol / l,the after 40 seconds 0,1 mol/lit, and after 1 minute 0,05 mol/lit. Calculate the average of speed response of to the three time phases.
given:
Δt1 = 20 sec
Δt2 = 40 sec
Δt2 = 1 min = 60 sec
с1(НВr) = 0,5 mol/lit
с2(НВr) = 0,3 mol/lit
с3(НВr) = 0,1 mol/lit
с4(НВr) = 0,05 mol/lit
find:
υ1 - ?
υ2 - ?
υ3 - ?
Solution:
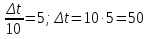
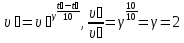
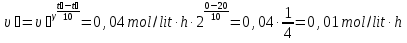
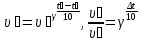
Answer: υ1 = 0,01 mol/lit · s
υ2 = 0,05 mol/lit · s
υ3 = 0,0008 mol/lit· s
-
After a certain period of time after the start of the reaction equation which СО2(g) + С(s) = 2СО(s), concentration of carbon oxide is reduced by 4 times. how many times this will reduce the reaction rate compared to the initial ?
given:
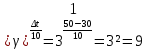
find:
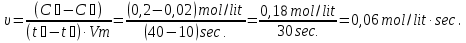
Solution:
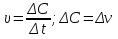
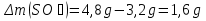
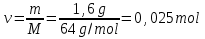
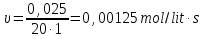
Answer: the reaction rate decreases 16 times .
-
A chemical reaction occurs in the solution according to the following equation: А + В = С. Initial concentrations :
A - 2 mol/lit, B - 2,5 mol/lit. After 20 minutes the concentration of A decreased to 1 mol/lit. What was of concentration of the substance in ?Determine the average rate of the reaction .
given:
Δt = 20 min
С1(А) = 2 mol/lit
С2(А) = 1 mol/lit
find:
С3(В) -?
υ1 - ?
Solution:
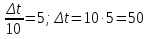
20 min = 20· 60= 1200 s
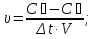
А + В = С
С1(А) = с1(В) = 2 mol/lit
С2(А) = с2(В) = 1 mol/lit
С2(В) = Сinitial(В) - Сend(В) = 2,5 mol/lit - 1 mol/lit = 1,5 mol/lit.
Answer: υ = 8 ·10-4mol/lit · s; С(В) = 1,5 mol/lit · s.
-
In the reacting system , the scheme of which
3А + В⇄ 2С + D, the of equilibrium concentration of the substance A, B and C are respectively 0,4, 0,9 and 1,2 mol/lit . Find the initial concentrations of substances A and B.
given:
[А] = 0,4 mol/lit
[В] = 0,9 mol/lit
[С] = 1,2 mol/lit
find:
С(А)исх.-?
С(В)исх. -?
Solution:
υ(А)исх = υ(А)прор. + υ(А)разн. = 1,8 mol + 0,4 mol = 2,2 mol
υ(В)исх = υ(В)прор. + υ(А)разн. = 0,6 mol + 0,9 mol = 1,5 mol
Answer: С(А)исх. = 2,2 mol/lit; С(В)исх. = mol/lit
-
Calculate the amount of carbon monoxide formed within for 50 seconds , if the rate of the reaction : C(t) + H2O(g) = CO(g) + H2(g) of the is 0,3 mol/lit · sec, and the reactor volume is equal 1 liter.
given:
V = 1 lit
τ = 60 sec
ν= 0,3 mol
find:
ν(СО)- ?
Solution:
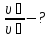
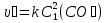
ν = υ · V · t
ν(СО) = 0,3 mol/lit · sec · 1 lit · 50 sec = 15 mol
Answer: ν(СО)= 15 mol.
-
How to change the speed of the reaction proceeding according to the equation : 2CO(g) + O2(g) = 2CO2(g), if:
a) the concentration of oxygen increased in 2 times ?
b) increase the concentration of carbon monoxide in 2 times?
а) given:
[О2] >in 2 times
find:
υ - ?
Solution:
υ = k[CO]2 · [O2]
1) с2(СО) = с1(СО)
2) с2(О2) = с1(О2) · 2
3) υ = k · с1(О2) · 2 = 2 mol/lit·sec.
Answer: When you increase the concentration of oxygen at 2 times the speed of reaction is increased in 2 times.
б) given:
[СО] >in 2 times
find:
υ - ?
Solution:
υ = k[CO]2 · [O2]
1) с2(СО) = с1(СО) · 22
2) с2(О2) = с1(О2)
3) υ = k · с1(О2) · с1(СО) · 22 = k ·4 = 4 mol/lit · sec.
Answer: When you increase the concentration of carbon monoxide at 4 times the speed of reaction is increased in 4 times.
-
How many times it is necessary to increase the concentration of the hydrogen sulfide, to the reaction rate 2Н2S(g) + SО2(g) = 2S(s) + 2Н2О(g) risen in the 9 times ?
given:
υ>in 9 times
find:
Δс(Н2S) - ?
Solution:
υ = k·с(Н2S)2 · с(SO2)
υ = k·с(Н2S)2 · с(SO2)
υ = 9 mol/lit · с (by condition problem)
1) с2(Н2S) = с1(Н2S) · х2
2) с2(SО2) = с1(SО2)
3) 9 mol/lit = k · х2
х = 3 mol/lit·s.
Answer: to increase the rate of this reaction is 9 times necessary to increase the concentration of hydrogen sulfide in 3 times.
-
Write an the expression depending on the speed of the forward and reverse reaction on the concentration reactants of the substances for the following processes :
а) 2SO3(g) ⇄ 2SO2(g) + O2(g)
b) FеO(кр) + СO(g) ⇄ Fе ( кр) + CO2(g)
How to change the speed of the forward and reverse reactions,
If the increase pressure system in 3 times ?
given:
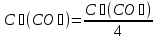
find:
Solution:
а) Homogeneous system , then the speed of forward and reverse reaction expressed respectively :
υ1 = k1 · [SO3]2 (direct reaction),
υ2 = k2 · [SO2]2 · [O2] (reverse reaction),
With increasing pressure in three times the concentration of substances also increased the by 3 times.
The rate of direct reaction after increasing pressure is expressed by:
υ1 = k1 · (3[SO3]2)
then,
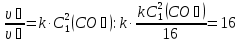
the rate of the forward reaction will increase by 9 times .
For the reverse reaction after increasing pressure 3 times the expression law of mass action will take the form :
υ2 = k2 · (3[SO3]2) · (3[О2]).
тогда,
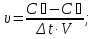
rate of the reverse reaction will increase by 27 times .
b) a heterogeneous system , then:
υ1 = k1 · [СO] (direct reaction),
υ2 = k2 · [СO2] (reverse reaction)
Consequently,
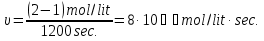
the rate of the forward reaction will increase by 3 times.
For the reverse reaction :
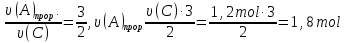
speed is also increased by 3 times.
Answer: a) the speed of the forward reaction increases by 9 times .
For the reverse reaction the rate increases to 27 times .
b ) the rate of the forward reaction will increase by 3 times.
For the reverse reaction speed is also increased by 3 times.
Basic concepts and stoichiometric laws of chemistry .
-
5 liters of nitrogen under a pressure of 2 atm , 2 l of oxygen under a pressure of 2.5 atm and 3 liters of carbon dioxide under a pressure of 5 atm of the mixed, the wherein volume of provided mixture equal to 15 liters . Calculate the pressures and is a mixture of the partial pressures of each gas.
given:
V1(N2) = 5 lit
P1 = 2 atm
V2(О2) = 2 lit
P2 = 2,5 atm
V3(СО2) = 3 lit
P3 = 5 atm
V4(mixture) = 5 lit
find:
P4 - ? P(N2) - ?
P(О2) - ? P(СО2) - ?
Solution:
From the law of Boyle - Mariotte
P1 ·V1 = P2 ·V2
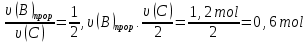
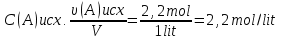
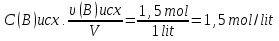
P4 = P(N2) + P(О2) + P(СО2) = 0,67 atm + 0,33 atm + 1,0 atm = 2 atm.
Answer: P4 = 2 atm,P(N2) = 0,67 atm, P(О2) = 0,33 atm, P(СО2) =1,0 atm.
-
Gas at 15 ° C and a pressure of 760 mm Hg.Art. occupies a volume 2 liters. Bring the volume gas to normal conditions .
given:
P1 = 750 mm Hg.art.
Т1 = 150 = 15 + 273 = 288
Т2 = 2730С
P2 = 760 mm Hg.art.
V1 = 2 lit
find:
V2 - ?
Solution:
On the basis of the combined Act defines volume V2
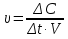
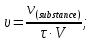
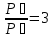
Answer: V2 = 1,9 lit.
-
A mixture consisting of 2 moles of hydrogen , some number the of moles of oxygen and 1 mol of nitrogen at 20 ° C and a pressure of 4 atm , occupies a volume of 40 liters. Calculate the number of moles of oxygen in the mixture and the partial pressure of each gas .
given:
ν1(Н2) = 2 mol
ν2(N2) = 1 mol
P = 4 atm
Т = 200С = 293 К
V(mixture) = 40 lit
find:
ν3(О2) - ? P(Н2) - ?
P(N2) - ?P(О2) - ?
Solution:
From equation Mendeleev - Clapeyron total number of moles of all the gases making up the mixture
The number of moles of oxygen in the mixture is equal to:
ν3(О2) = νmixture - ν1(Н2) - ν2(N2) = 6,66 mol - 2 mol - 1 mol = 3,66 mol.
The partial pressure each of gas calculated by the equation :

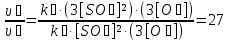
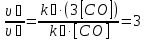
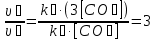
Answer: ν3(О2) = 3,66 mol;P(N2) = 0,6 atm, P(О2) = 2,2 atm, P(Н2) =1,2 atm.
-
In a 500 ml flask at 25 ° C is of 0.615 g of nitric oxide (II). Is gas pressure in the flask ?
given:
V = 500 ml = 0,5 lit = 0,5 ·10-3m3
m = 0,615 g
Т = 200С = 293 K
М(NO) = 30 g/mol
find:
P- ?
Solution:
From equation Mendeleev - Clapeyron find :
Answer:101592,6 Па.
24