- Учителю
- Lesson plan for 10th grade physics Uniform motin. + problems
Lesson plan for 10th grade physics Uniform motin. + problems
|
Class |
10th grade |
Date |
| ||
|
Lesson |
Physics | ||||
|
Period |
1 hour | ||||
|
Subject |
</<span>Uniform motion | ||||
|
Aim |
To study Uniform motion | ||||
|
Materials |
Mechanics | ||||
|
Methods and Techniques |
| ||||
|
Explaining, solving exercises | |||||
|
General Review of Previous Lesson : |
| ||||
|
Ask a few questions about last topic as : Uniform motion
| |||||
|
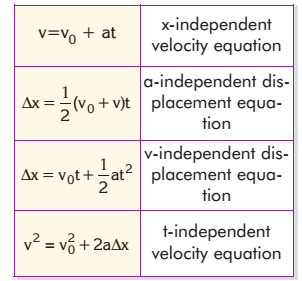
The following equations of kinematics are used to define uniformly accelerated motion: where a is the constant acceleration v0 is the initial velocity v is the final velocity x is the displacement t is the time The change in the position of an object is called the displacement which is also a vector quantity. Displacement is defined by 1. Two automobiles are 150 kilometers apart and traveling toward each other. One automobile is moving at 60 km/h and the other is moving at 40 km/h mph. In how many hours will they meet? (1.5) 2. A car travels 40 kilometers at an average speed of 80 km/h and then travels 40 kilometers atan average speed of 40 km/h. The average speed of the car for this 80-km trip is: (53 km/h) 3. In astronomy the light-year is used as a unit of distance. It is the distance that light can travel in one year. (For instance, our galaxy, the Milky Way, is about 150 000 light-years across). If light travels at a constant speed of 300 000 km/s, Calculate 1 light-year in km? 4.A car moving with an initial velocity of 25 m/s north has a constant acceleration of 3 m/s2 south. After 6 seconds its velocity will be: 5.A car, initially at rest, travels 20 m in 4 s along a straight line with constant acceleration. The acceleration of the car is: 2.5m/s2
| |||||
|
Evaluation: |
Ask guestions and give marks | ||||
|
| |||||